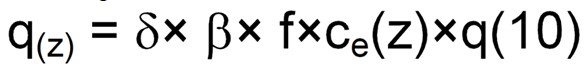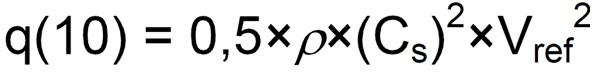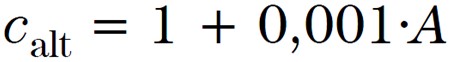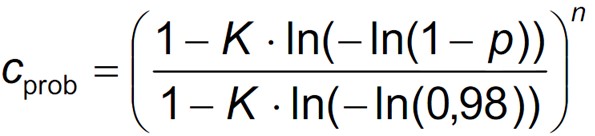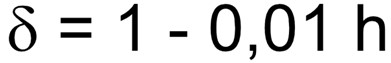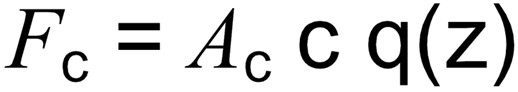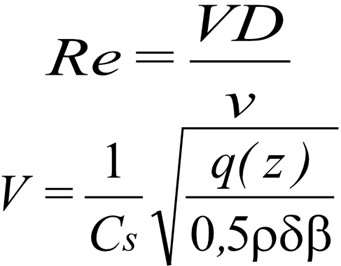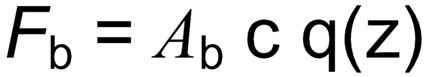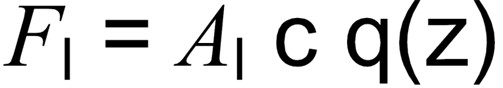Street light foundation wind loading design is the first step in street light foundation design. This determines the forces acting on the street light. The CivilWeb Street Light Foundation Design Spreadsheet calculates these forces in accordance with the procedure contained within BS EN 40-3-1. In the UK there is also a simplified wind loading method included in the national annex which removes many of the detailed inputs required by the full wind loading method and replaces them with a generalised maximum wind loading for each region of the UK. The CivilWeb Street Light Foundation Design Spreadsheet includes both methodologies which the user can choose between as appropriate.
Street Light Wind Loading - Detailed Design Procedure
The detailed method for calculating the wind loads acting on the street light is shown below. This is taken from BS EN 40-3-1. The wind pressure acting on the street light is calculated using the following equation with each parameter described in the following sections.
Reference Wind Pressure (q(10))
The reference wind pressure is determined from the following equation;
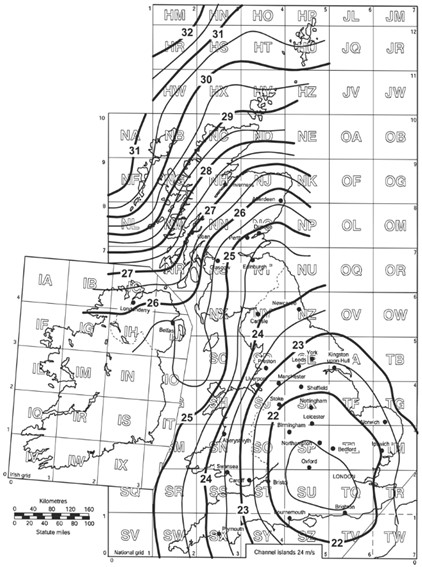
Vref is the 10 minute mean wind velocity at 10m above ground level for terrain category II, with a return period of 50 years. Vref is in turn calculated using the following equation where Vref,0 is the basic wind reference value which can be taken from the wind maps presented in BS EN 1991-1-4 NA and reproduced below and CALT is the altitude factor described below.
The Altitude Factor (Calt) can be determined from the below equation suitable for street lights, where A is the altitude of the site in metres above sea level.
The probability factor (Cs) is used to convert the reference return period from 50 years to any other return period. BS EN 40-3-1 recommends that a return period of 25 years is typically used for street lights. This is done using the below equation where K is the shape parameter equal to 0.2, n is the exponent equal to 0.5 and p is the probability of the event occurring in a given year (1 / return period). Note for a typical street light return period of 25 years the probability factor can be taken as 0.920.5.
The air density (ρ) is also required to calculate the wind pressure. BS EN 1991-1-4 and BS EN 40-3-1 recommends an air density value of 1.25kg/m3. In the UK a value of 1.226 has been used historically and is still recommended in the UK National Annex.
Column Size Factor (δ)
The column size factor makes an allowance for the fact that larger surface areas are less likely to be subject to the full design wind pressure over the whole area. The surface area of a street light is largely dictated by its height, for this reason the column size factor can be determined using the below equation where h is the street light height;
Dynamic Behavior Factor (ß)
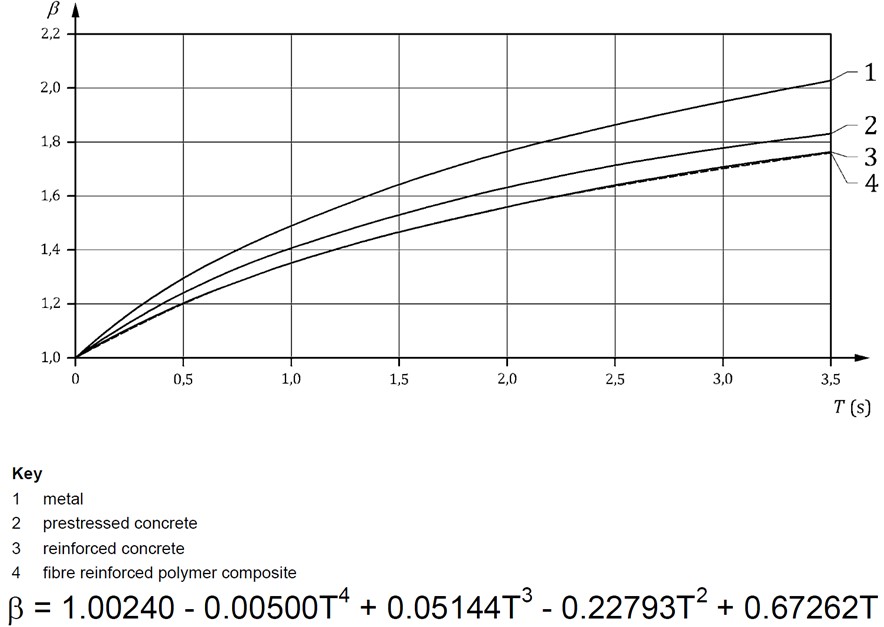
The dynamic behavior factor allows for the damping effects of the street light and the period of vibration which results from the dynamic behavior of the street light when subjected to loading from high winds. This value can be obtained either from the graph or the equation presented below. Note that the time of vibration of the street light (T) must be obtained from the column manufacturer or from testing. A value between 0 and 3.5 seconds is typical for street lights.
Topography Factor (f)
The topography factor is given as 1.0 for general cases. If topography is significant the procedures in BS EN 1991-1-4 can be followed to derive an appropriate topography factor.
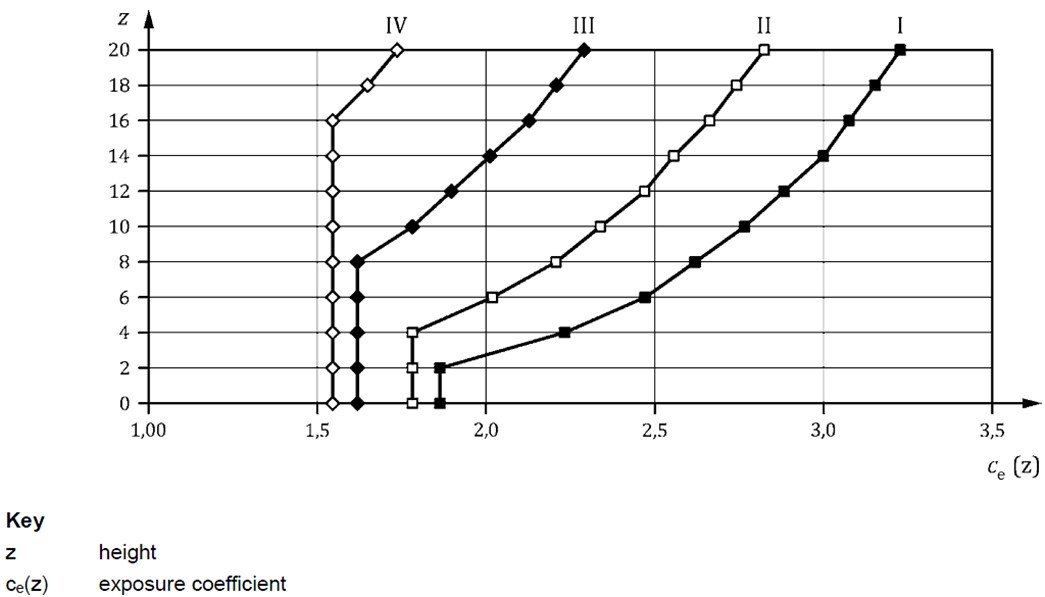
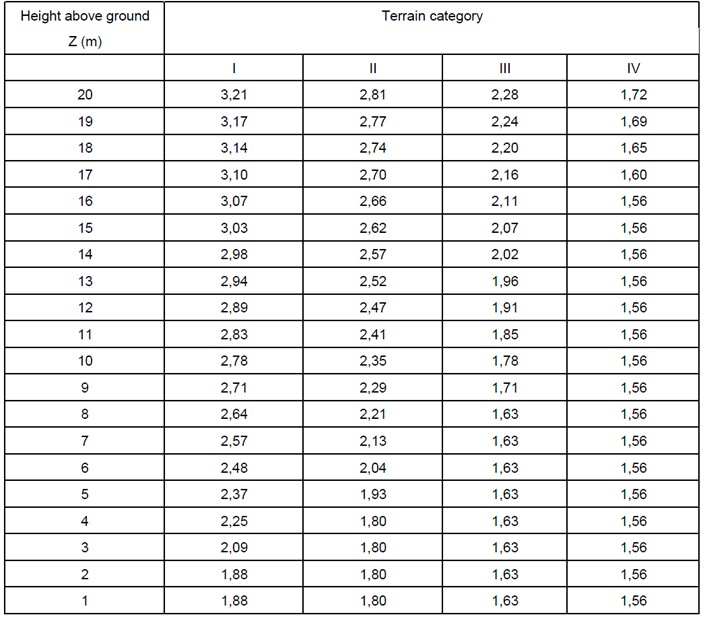
Exposure Coefficient (Ce(z))
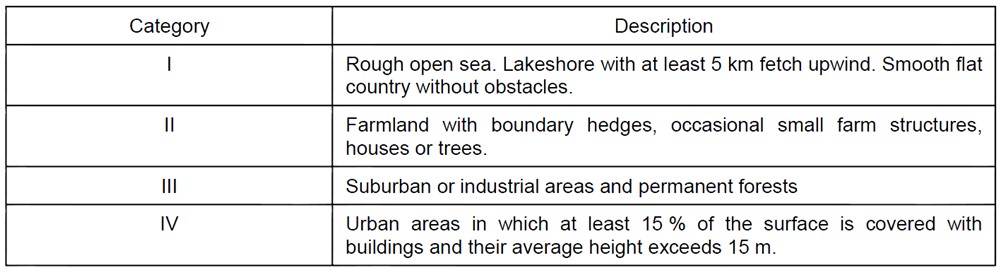
The exposure coefficient accounts for the variation in wind pressures relative to height above ground. The exposure coefficient is dependent on the terrain type, which can be selected from the below table.
The CivilWeb Street Light Foundation Design spreadsheet calculates the exposure coefficient directly using the below equations;
Alternatively the exposure coefficient can also be taken from either the table or graph below.
Street Light Wind Loading Horizontal Force
Once the wind pressure (q(z)) acting on the street light is calculated as above this can be used to calculate horizontal forces acting on the street light from wind actions.
Wind Loading - Street Light Column
The total wind loading horizontal force on the street light column shaft (Fc) can be calculated from the following equation where c is the shape coefficient and Ac is the projected area on a vertical plane normal to the wind direction, c is the shape coefficient derived as below and q(z) is the design wind pressure derived as in the previous section.
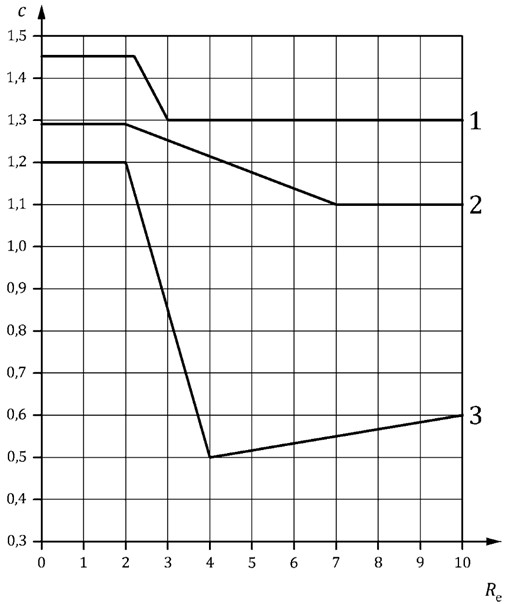
Shape Coefficient (c)
The shape coefficient takes account of the variation in the action of the wind depending on the shape of the object, in this case a street light column. The shape factor can be taken from the following graph;
Re is the Reynolds number calculated in accordance with the below equation where D is the street light column diameter or distance across flats, v is the kinematic viscosity of air usually taken as 15.1x10-6 m2/s, and V is the wind speed as calculated in the below equation.
The shape coefficient for the luminaires can be taken from manufacturer’s information or from testing. Where this information is not available a shape coefficient value of 1.0 should be used.
Wind Loading - Street Light Bracket
The total wind loading horizontal force acting on the street light bracket (Fb) can be calculated from the following equation where Ab is the projected area of the bracket on a vertical plane normal to the direction of the wind, c is the shape coefficient and q(z) is the design wind pressure.
Wind Loading - Street Light Luminaires
The total wind loading horizontal force acting on the column bracket (Fl) can be calculated from the following equation where Al is the projected area of the bracket on a vertical plane normal to the direction of the wind, c is the shape coefficient and q(z) is the design wind pressure.
Street Light Wind Loading - Bending Moments
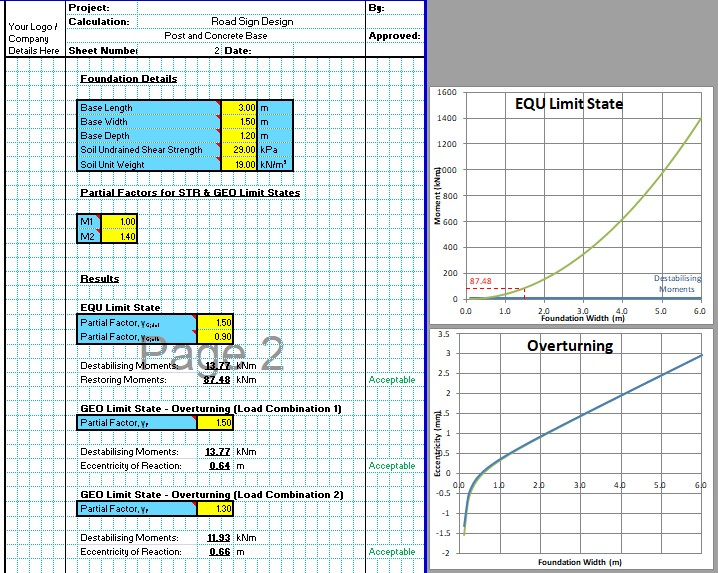
The horizontal forces acting on the street light calculated above can now be converted to bending moments with the maximum moment occurring at the base of the street light for surface mounted street lights or at a depth of the planting depth divided by √2.
The CivilWeb Street Light Foundation Design spreadsheet divides the street light column into 20 separate sections in order to analyse the effects of any changes in section. Typically street light columns include a wider base section and a narrower top section which can be accommodated in the spreadsheet. The bending moments for these 20 sections are added to those from the street light bracket and the luminaire to calculate to maximum bending moment acting on the whole street light.
Street Light Wind Loading – Simplified Method
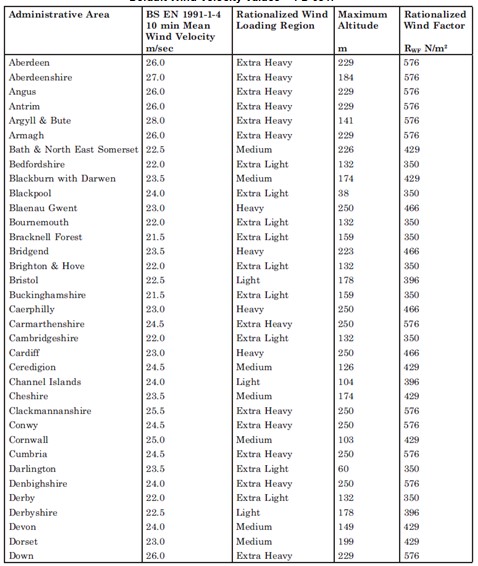
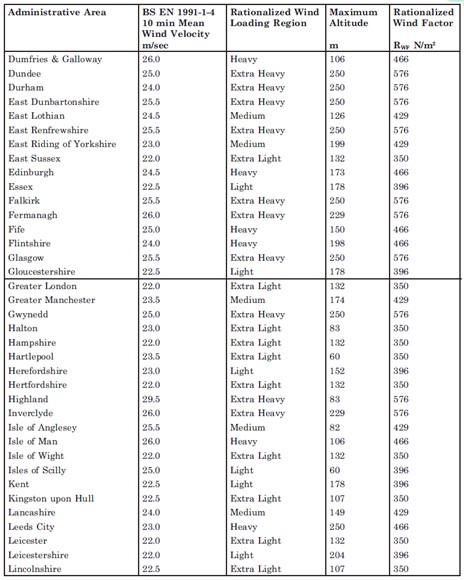
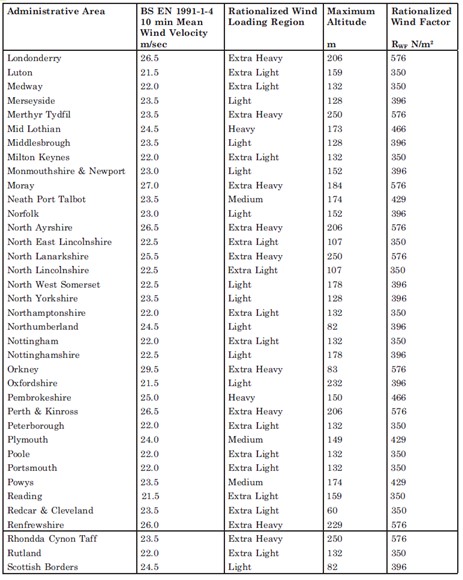
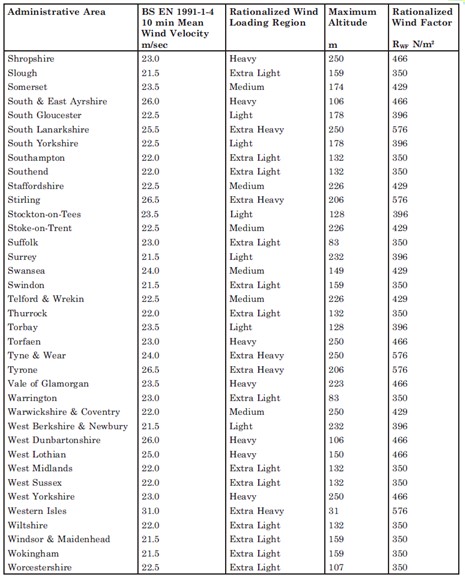
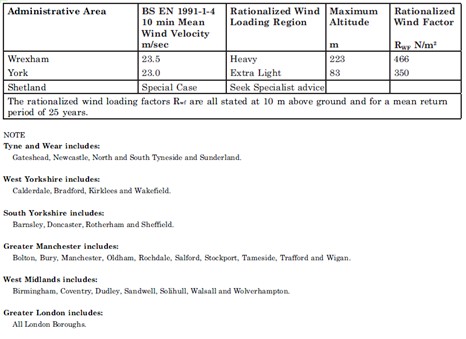
An alternative to the detailed method exists. Rationalized Wind Load Factors have been compiled for each area of the UK. These factors replace the detailed calculation of q(10) as in the previous section with a standardized wind load suitable for the whole area. This was then further standardized into five categories from Very Low, Low, Medium, Heavy and Very Heavy. These wind load factors are shown at the bottom of this page.
The design procedure is further simplified by assuming values for the air density and kinematic viscosity and assuming a 25 year return period. This represents a massively simplification of the design procedure and is useful for standard applications where detailed site information is not available. However as with all standardized design methods this is inherently conservative and much more economical solutions can be acquired in some cases by completing the more detailed design procedure.
CivilWeb Street Light Foundation Design Spreadsheet
The CivilWeb Street Light Foundation Design Spreadsheet includes both the full detailed methodology and the simplified method. This enables the designer to choose the most appropriate method to suit the design conditions. In most cases this will be the detailed method. While this method is much more detailed and involves many more inputs it is much more accurate and the CivilWeb Street Light Foundation Design Spreadsheet includes guidance to make the detailed design procedure as quick and easy as possible.
Or why not bundle the CivilWeb Street Light Foundation Design Spreadsheet with our Sign Post Foundation Design Calculator for only £5 extra?
Download Free Trial Version
To try out a fully functional free trail version of this software, please Click Here or enter your email address below to sign up to our newsletter.