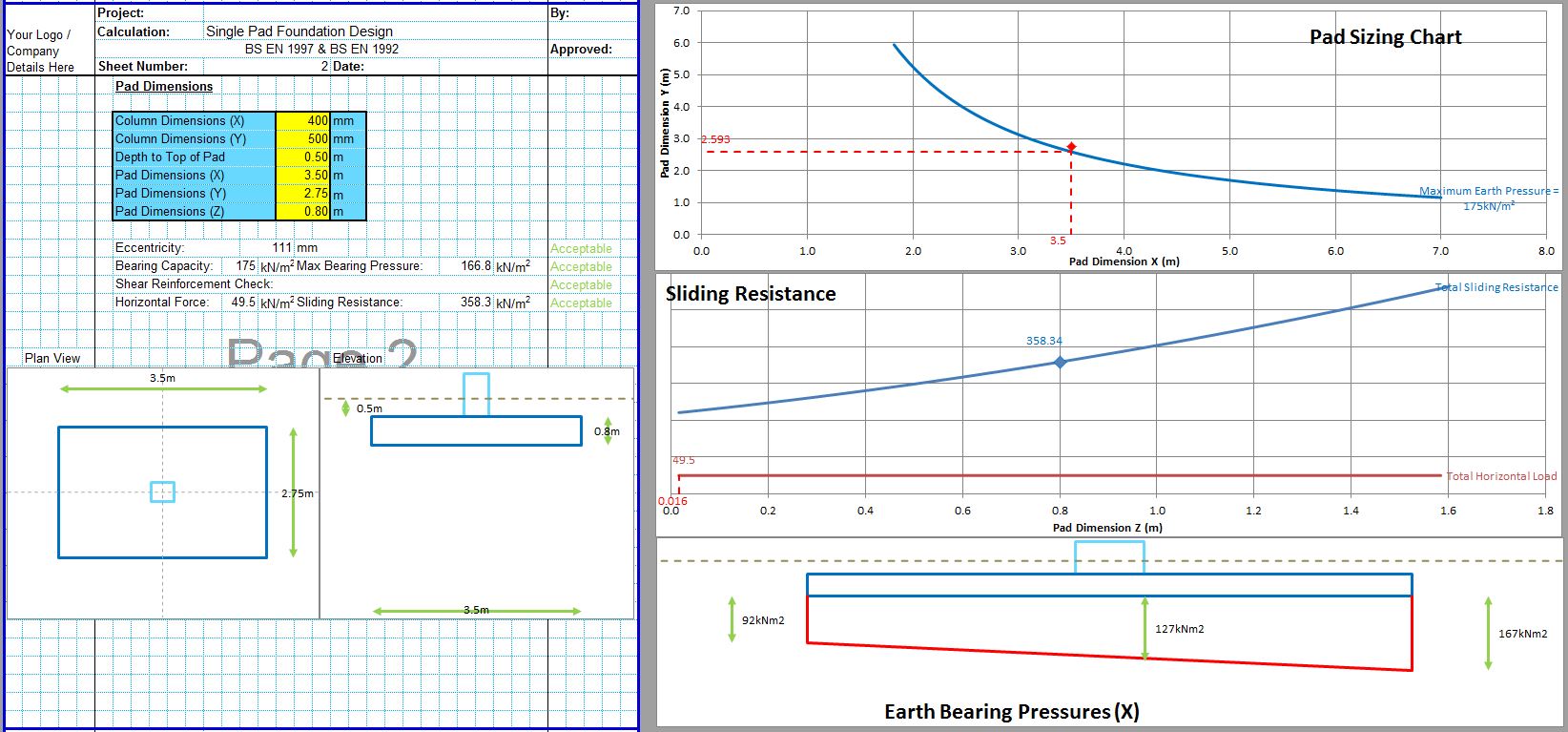
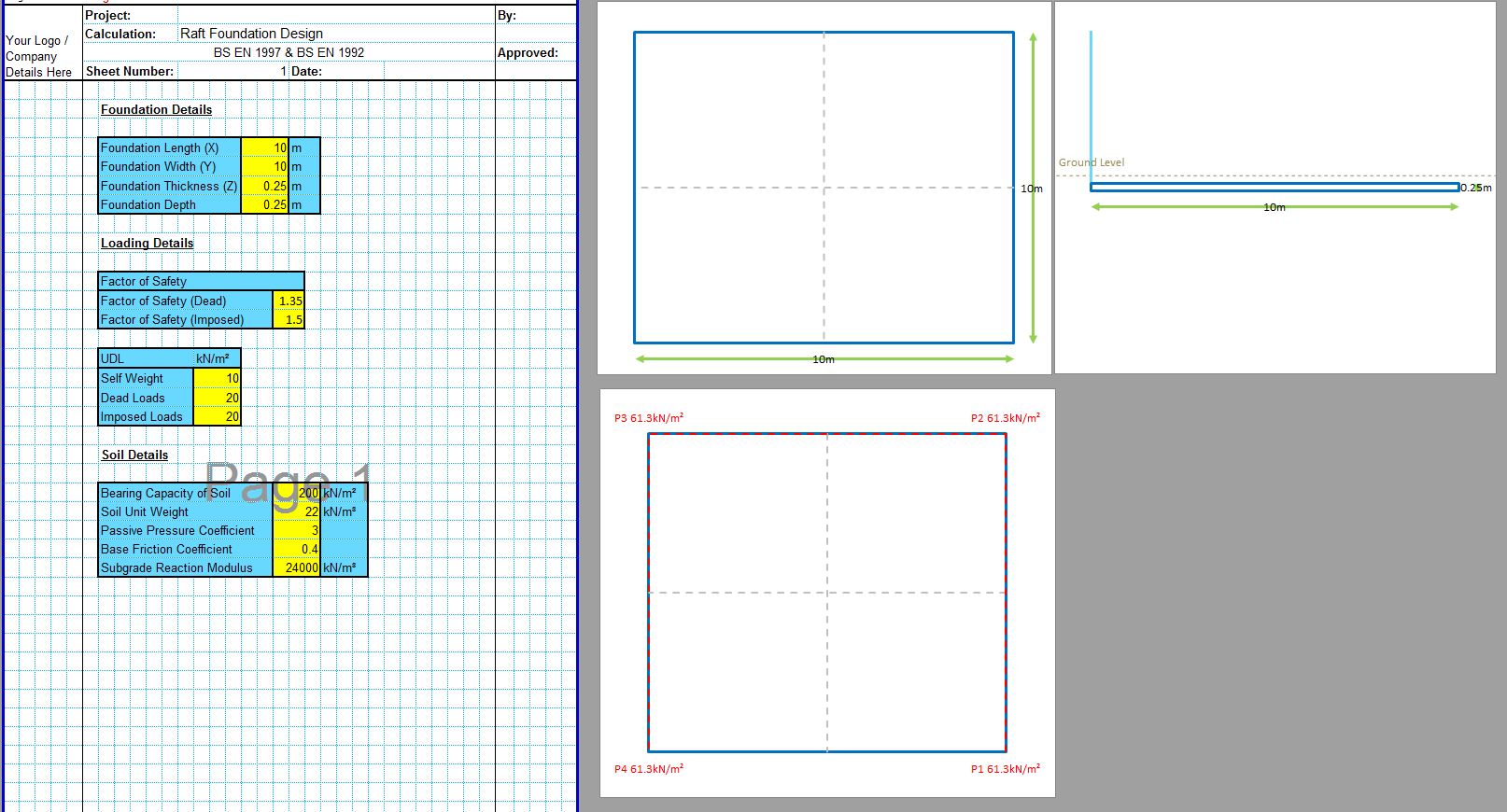
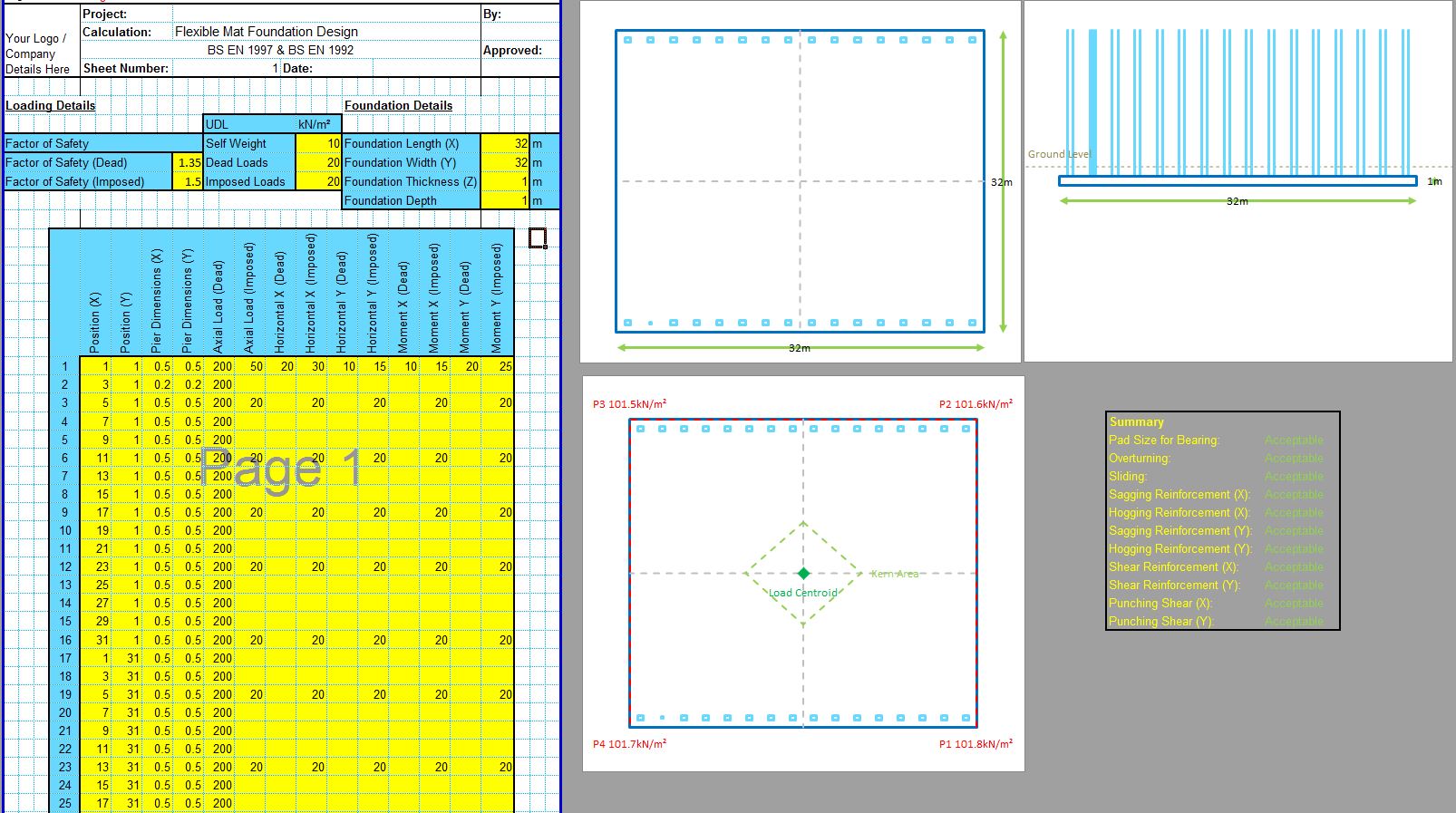
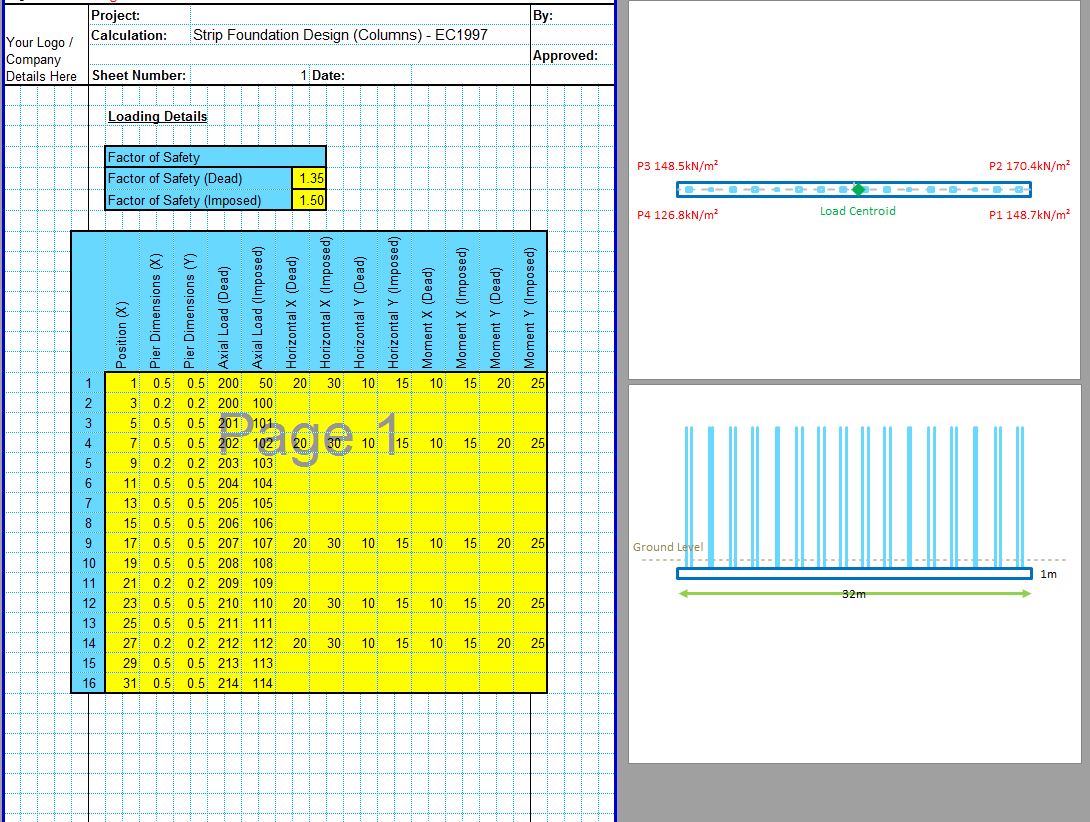
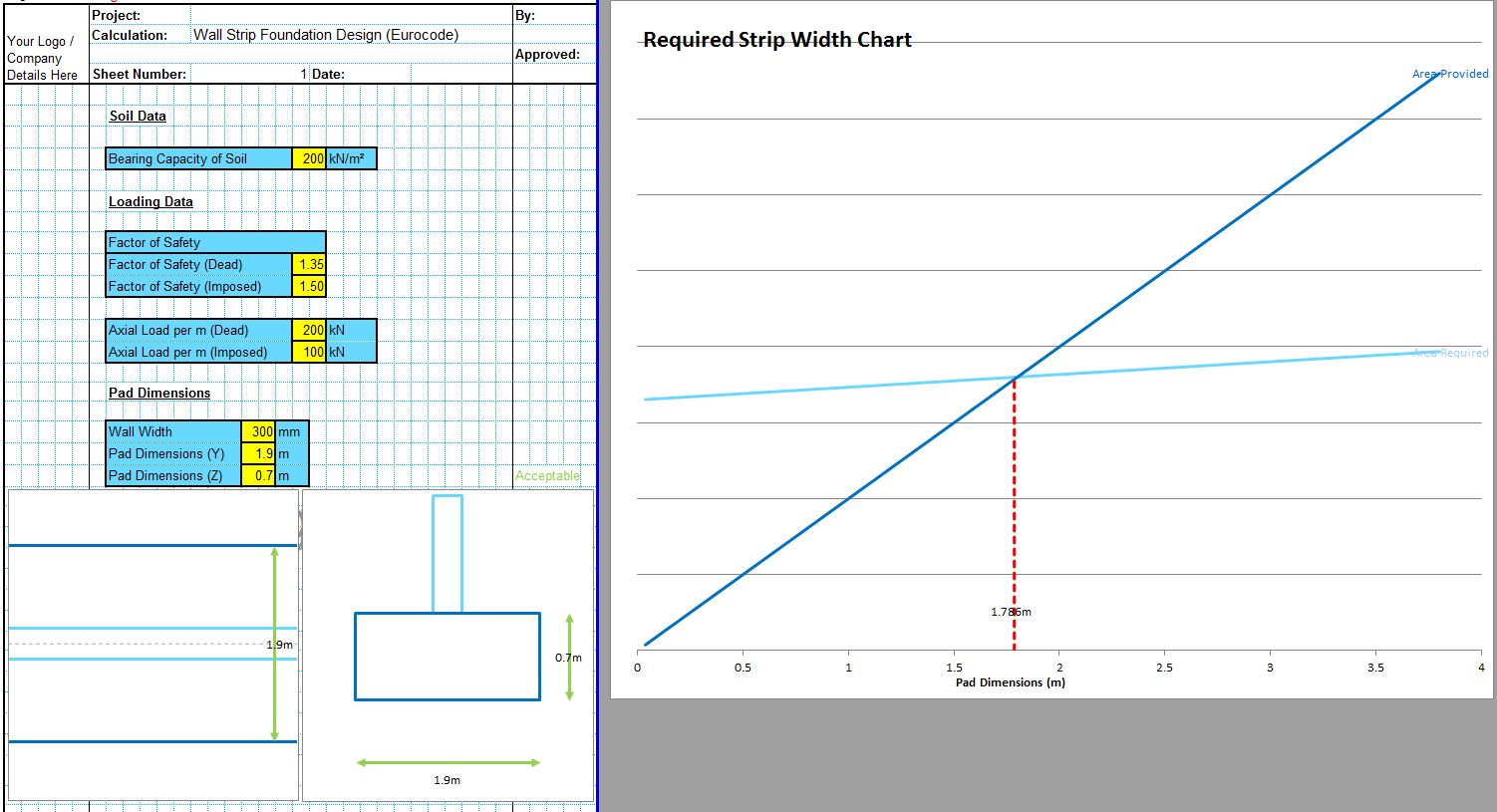
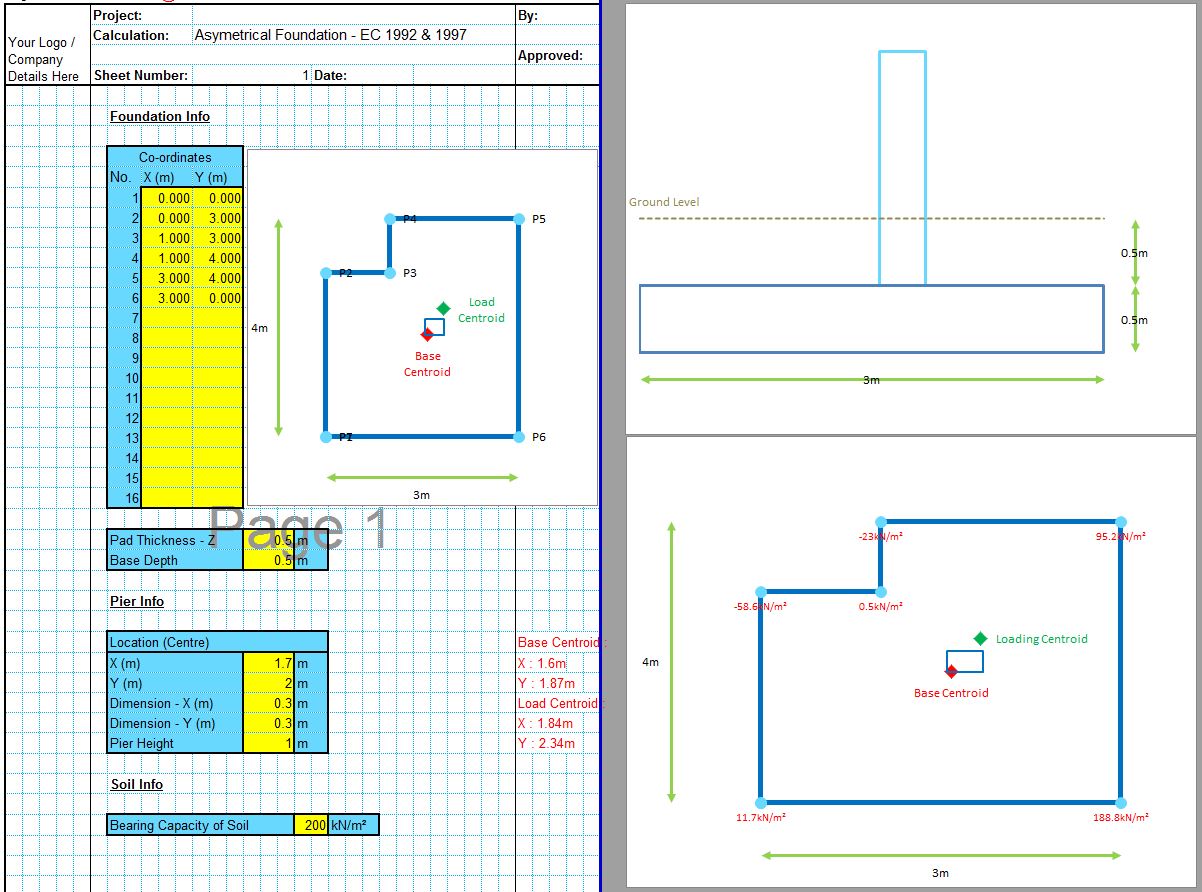
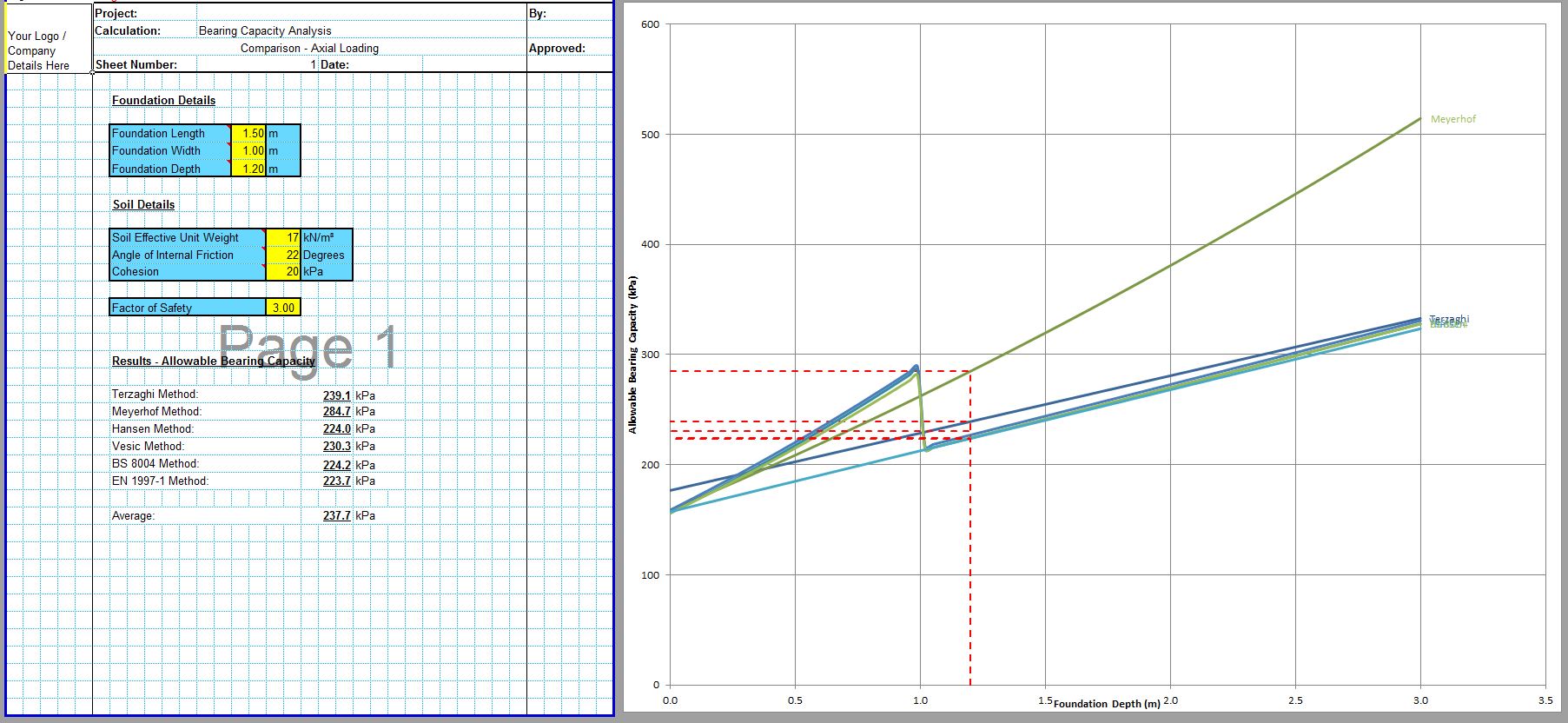
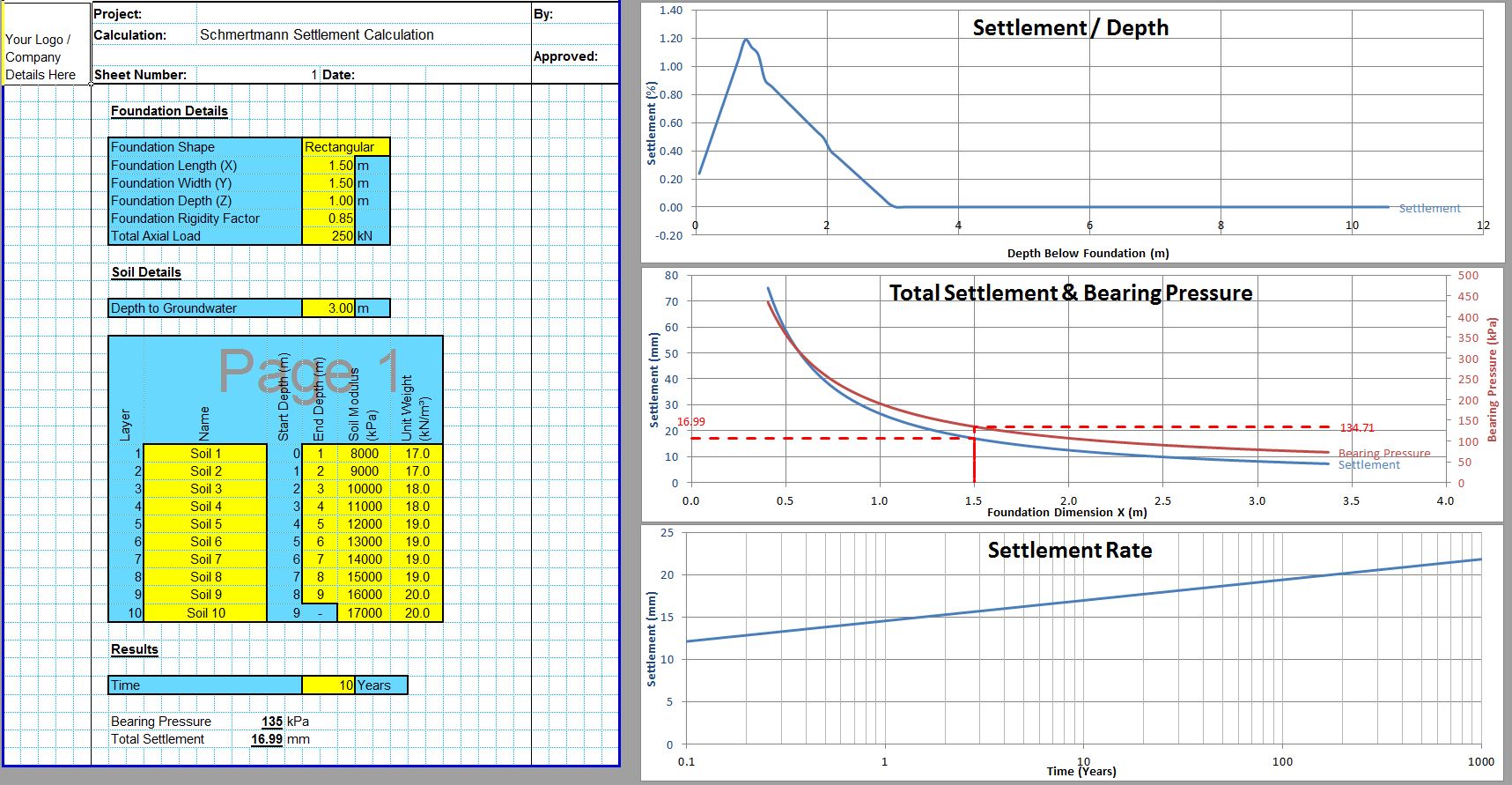
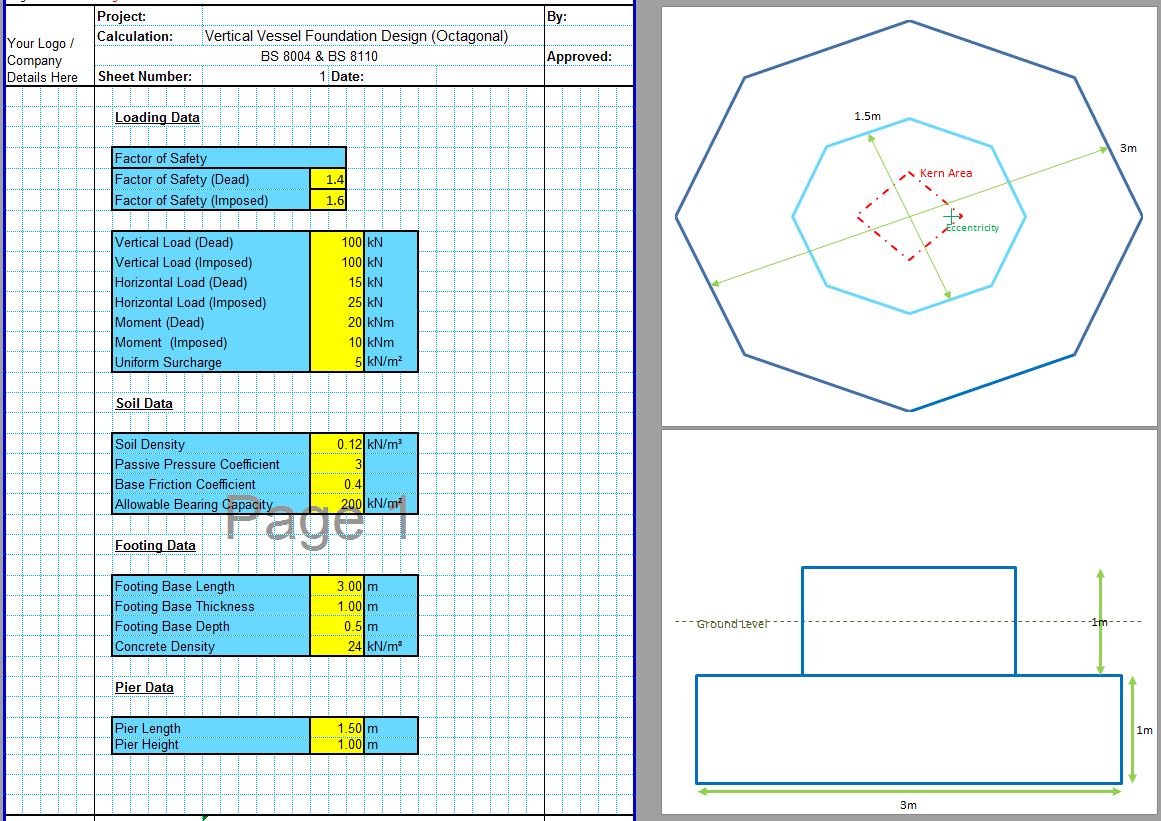
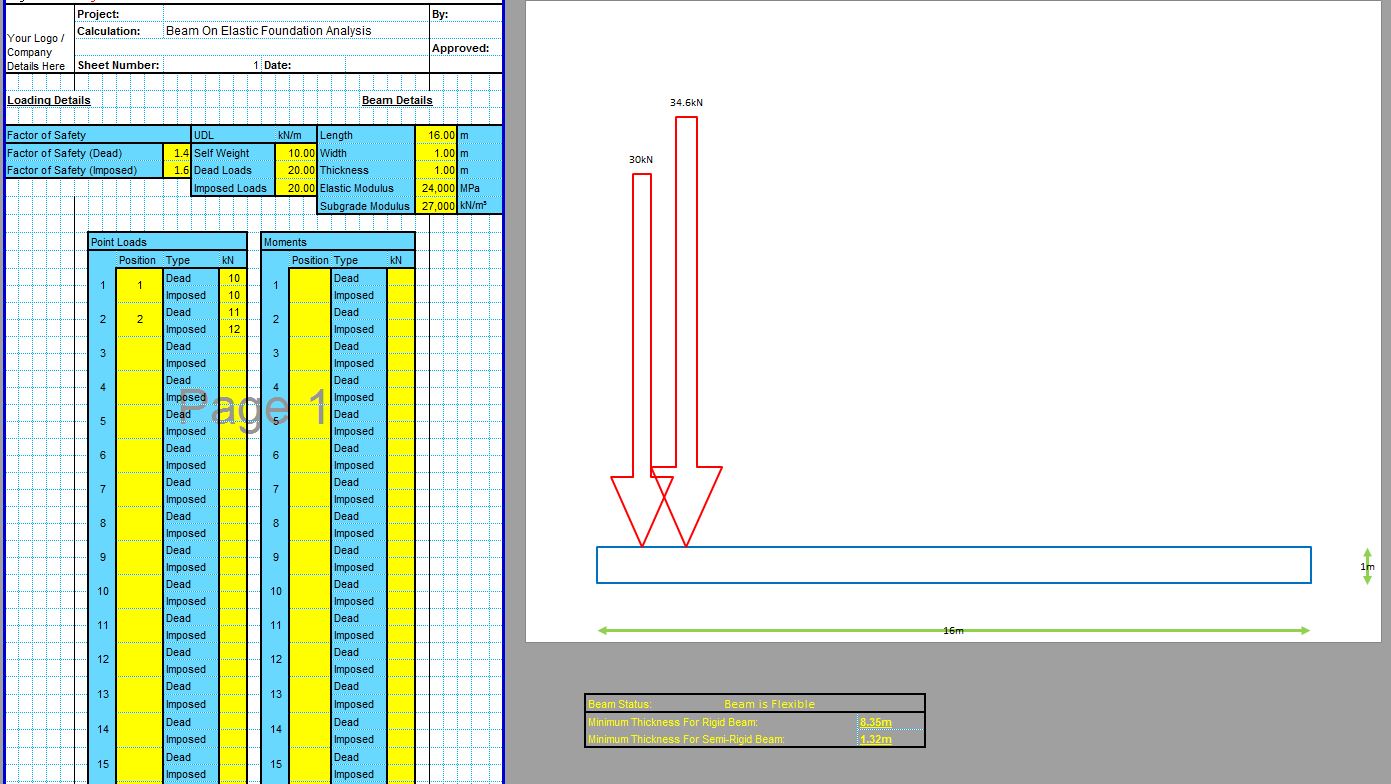
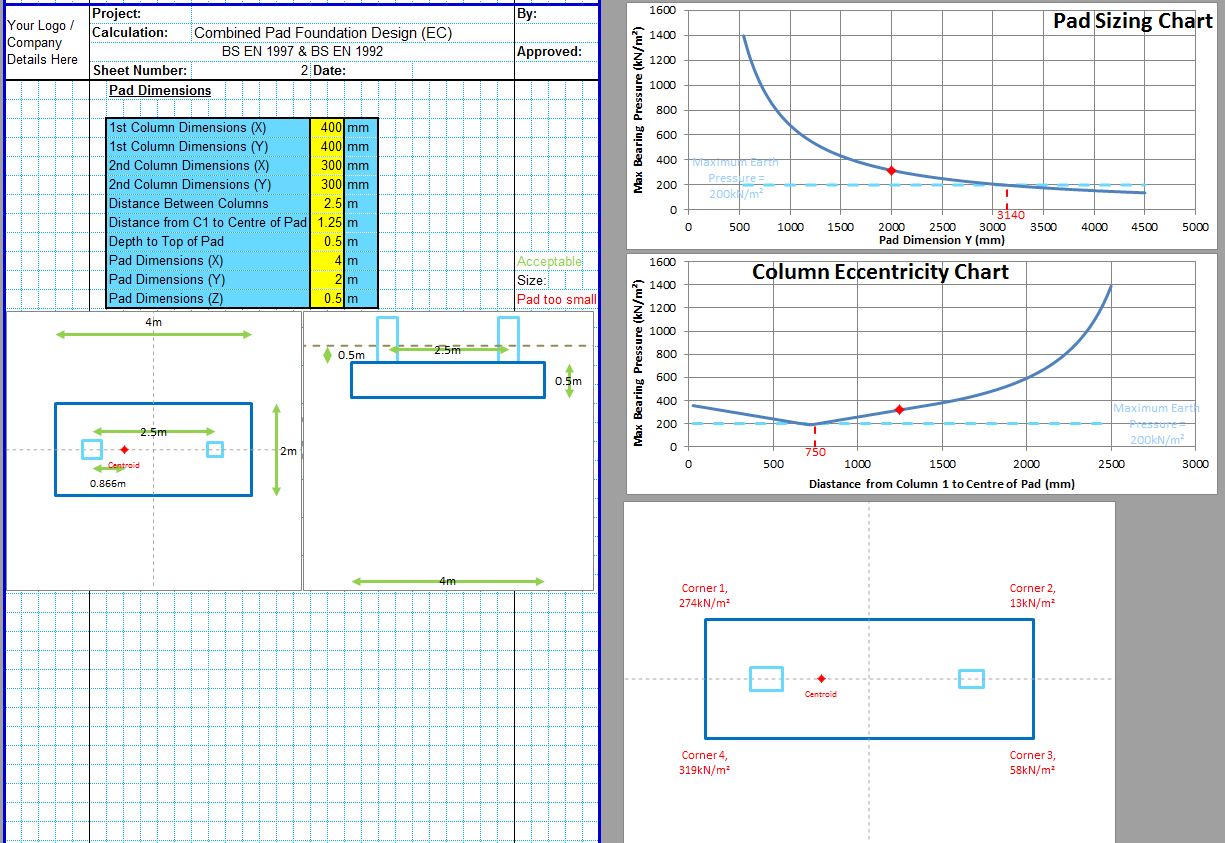
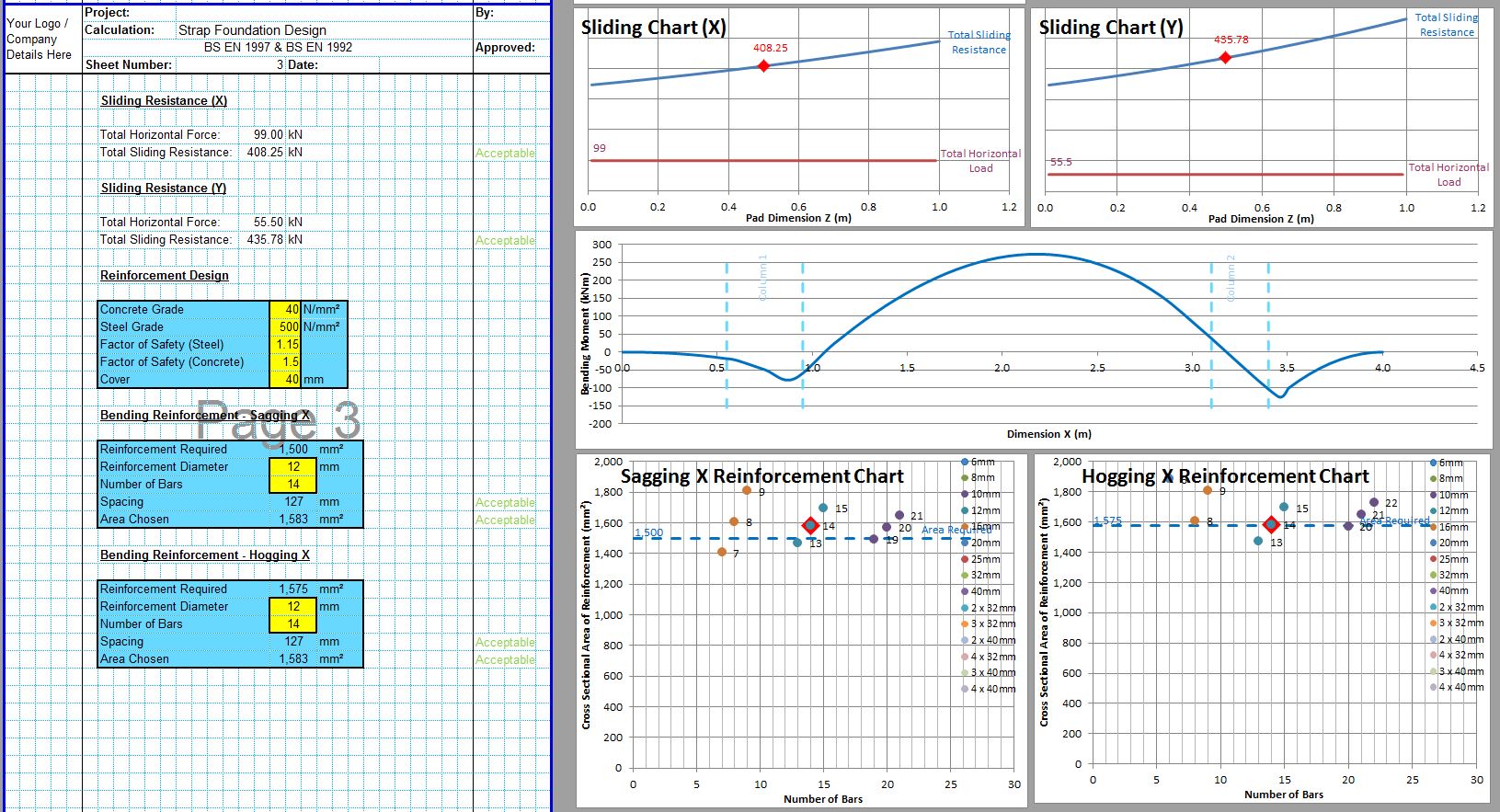
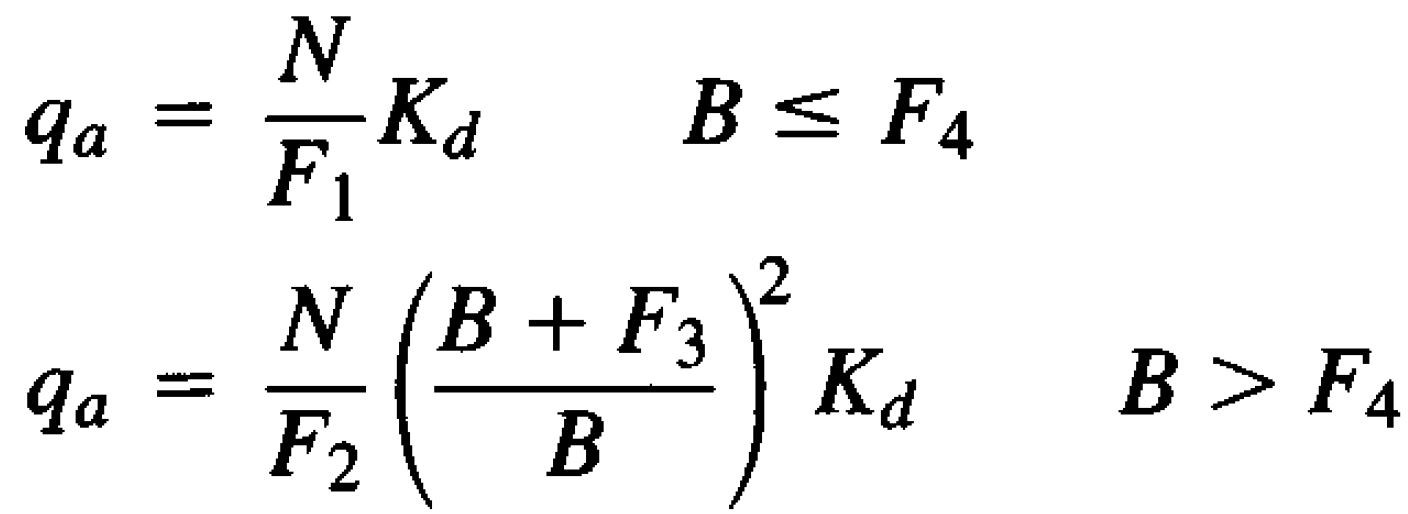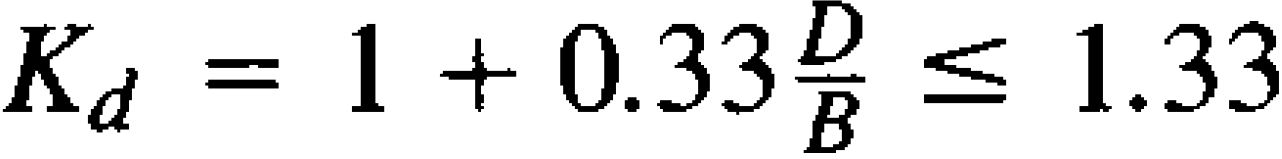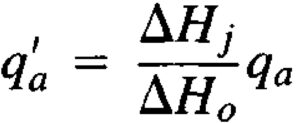The CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation from SPT Value XLS Spreadsheet can be used to convert the SPT n value to the bearing capacity of the soil. The spreadsheet uses a procedure developed by Bowles based on the Meyerhof and Terzaghi methods to calculate the bearing capacity of the soil from the SPT value. This is particularly useful for granular soils where undisturbed samples can be difficult to obtain. The spreadsheet completes the calculations instantly allowing the designer to convert the SPT value to the bearing capacity in minutes.
The CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation from SPT Value XLS Spreadsheet also includes unique analysis tools which allow the designer to see at a glance exactly what effects different sized foundations will have on the soil bearing capacity allowing an optimised design to be completed easily. The spreadsheet is included in the Soil Bearing Capacity from SI Info Spreadsheet Suite which can be purchased at the bottom of this page for just £10. Alternatively the full CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation Excel Suite including 9 different methods including the SPT value method can be purchased together for just £20.
Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation from SPT Value
In granular soils it can be very difficult to obtain undisturbed samples for testing in a laboratory. This makes it difficult to apply the above bearing capacity methods because the soil parameters will not be reliable. In this case it is common practice to use site investigation information such as SPT or CPT results in order to determine the allowable bearing capacity.
The Standard Penetration Test (SPT) is used to assess the density of a sandy soil. The test involves using a split barrel sampler which is driven into the soil at the bottom of a cased borehole. The SPT test procedure is detailed in BS 1377 Part 9 or ASTM D-1586.
The number of blows to drive the sampler 300mm in to the soil is recorded. This is called the standard penetration resistance or N number of the soil. The N number can then be converted using empirical methods to an allowable bearing capacity.
Allowable Soil Bearing Capacity Equations from SPT Values
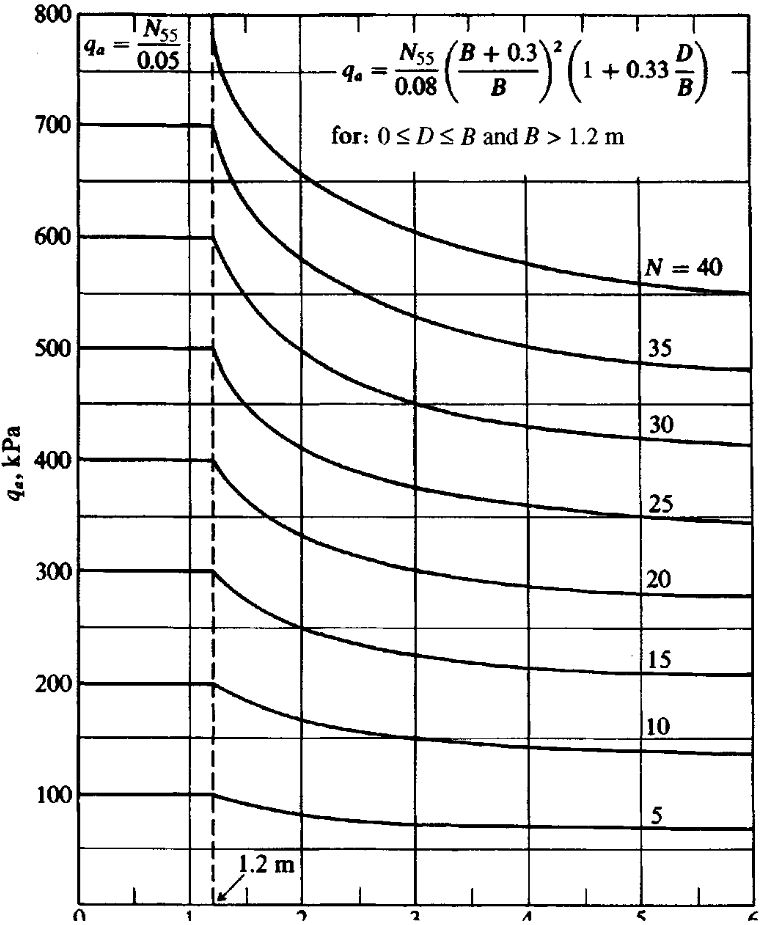
Several empirical methods have been developed to convert SPT values into allowable bearing pressures. Terzaghi and Peck and Meyerhof developed similar methods in the 1960s and 1970s. These methods were designed to obtain allowable bearing pressures which would limit settlement to a maximum of 25mm, with differential settlement a maximum of 75% of the maximum. These methods were widely used however experimental and field observation data has shown them to be overly conservative (around 50%).
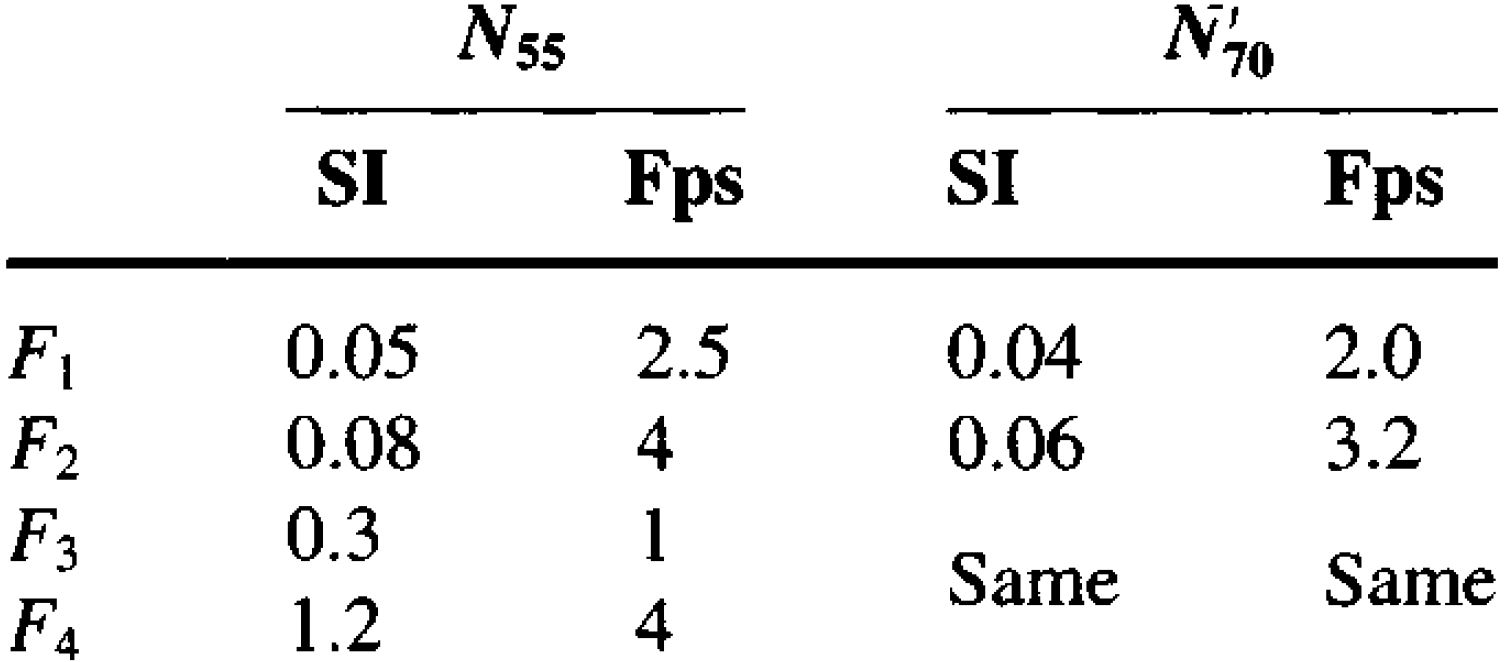
Bowles adjusted these methods by 50% to obtain the below equations where qa is the allowable bearing pressure, D is the foundation depth and B is the foundation width;
The settlement is assumed to be directly proportional to the bearing pressure. So this allowable bearing pressure value can be adjusted to suit any allowable settlement using the below equation where ΔH0 is 25mm and ΔHj is the allowable settlement.
This equation has been converted into a graph for ease of use, see below.
SPT N Value to Use
This method uses a single N value which must be representative of the soil. The zone of soil affected by the foundation is typically taken as between 0.5 x the foundation width above the foundation base to a depth of 2 x the foundation width below the base. The N value used can be an average value over this depth, with care taken if there are any large deviations. The choice of N value may need to be iterative if the foundation width is adjusted as this will also adjust the influence zone of the foundation.
Care must also be taken where there are areas of significantly lower N value below the foundation influence zone as this can lead to higher than expected settlements. In this case the N value used in the calculations should be adjusted.
SPT N Value Adjustments
In order to ensure that the N values used for design are representative, further adjustments are often required. The most commonly applied adjustments are for overburden pressure and groundwater level.
Alternative Methods
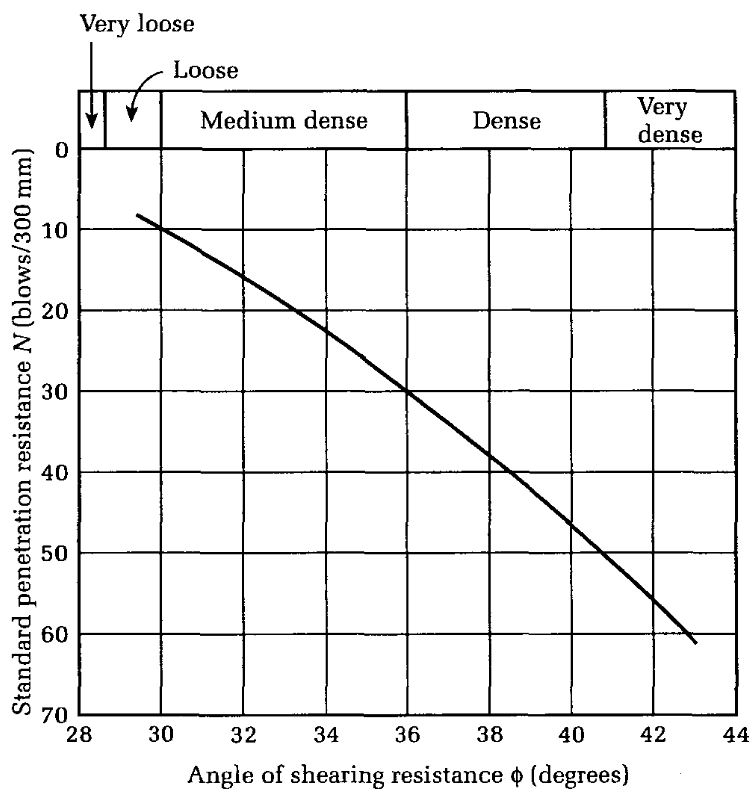
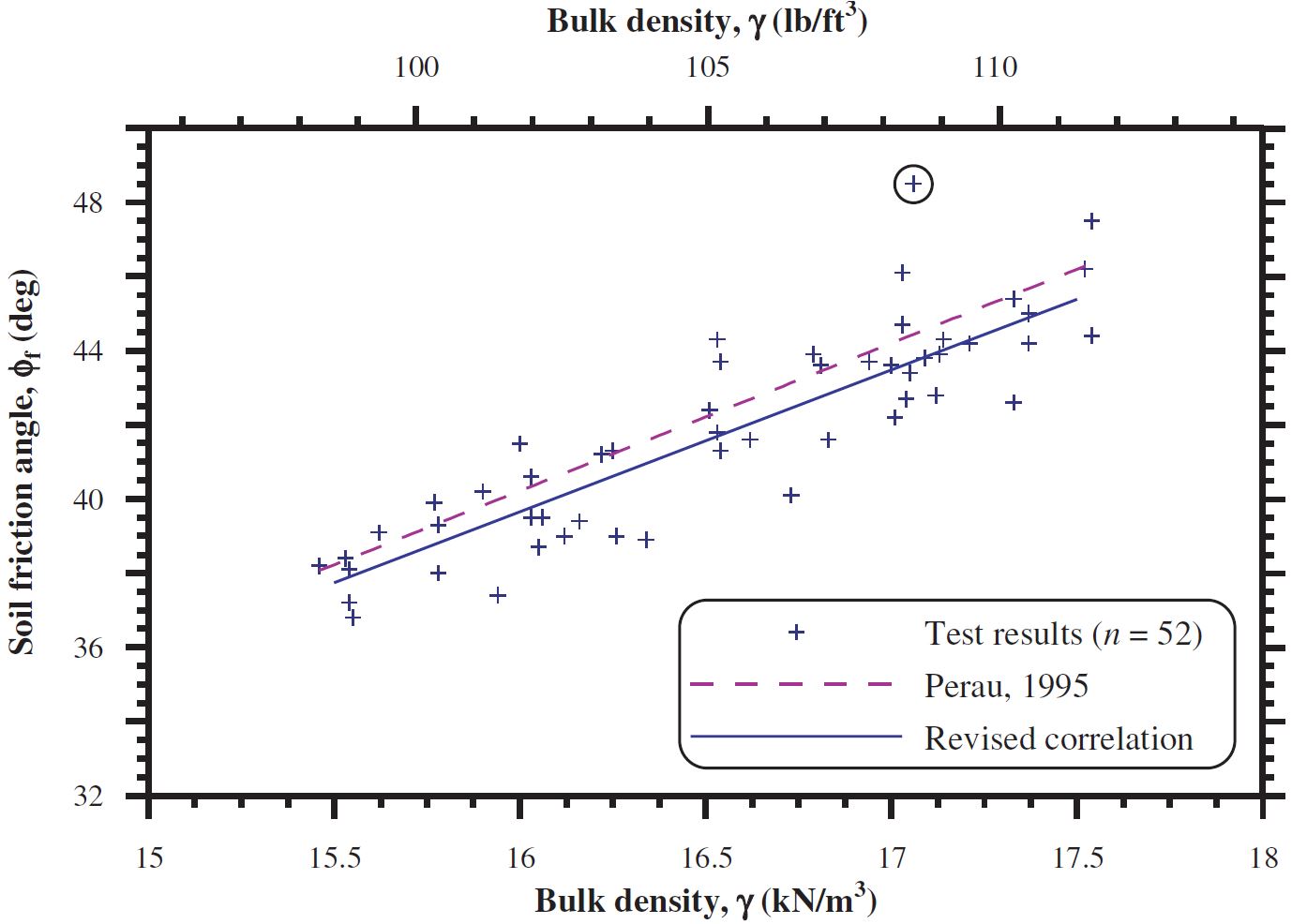
One alternative to this empirical method is to use SPT values to estimate the soil parameters required for the analytical methods. SPT results can be converted into an estimate of the soils angle of shearing resistance and unit weight. One relationship published by Peck is shown below with a corresponding relationship between angel of shearing resistance and bulk density.
CivilWeb Soil Bearing Calculation from SPT Value XLS Spreadsheet
The CivilWeb Soil Bearing Calculation from SPT Value XLS Spreadsheet allows the user to estimate the bearing capacity of a soil from its SPT n value. This is useful in coarse granular soils where representative or undisturbed samples cannot always be recovered for laboratory testing. The spreadsheet also includes unique analysis tools which allow the designer to complete a fully optimised bearing capacity calculation in minutes without time consuing iterative hand calculations.
The CivilWeb Soil Bearing Calculation from SPT Value XLS Spreadsheet is included in the Soil Bearing Capacity from SI Info Spreadsheet Suite which also includes methods of estimating the soils bearing capacity from CPT data and plate load test data.
Buy the Soil Bearing Capacity from SI Info Spreadsheet Suite now for only £10.
Purchase the full Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation Spreadsheet Suite including 9 different methods for only £20.
Or buy our best value bundle, the full Foundation Design Suite including all 12 of our foundation design spreadsheets at a discount of 80%.
Download Free Trial Version
To try out a fully functional free trail version of this software, please enter your email address below to sign up to our newsletter.
Other Foundation Design Spreadsheets;
Foundation Design Spreadsheet Suite
Our full Foundation Design Suite includes all 12 of our foundation design spreadsheets for only £50 (80% discount).