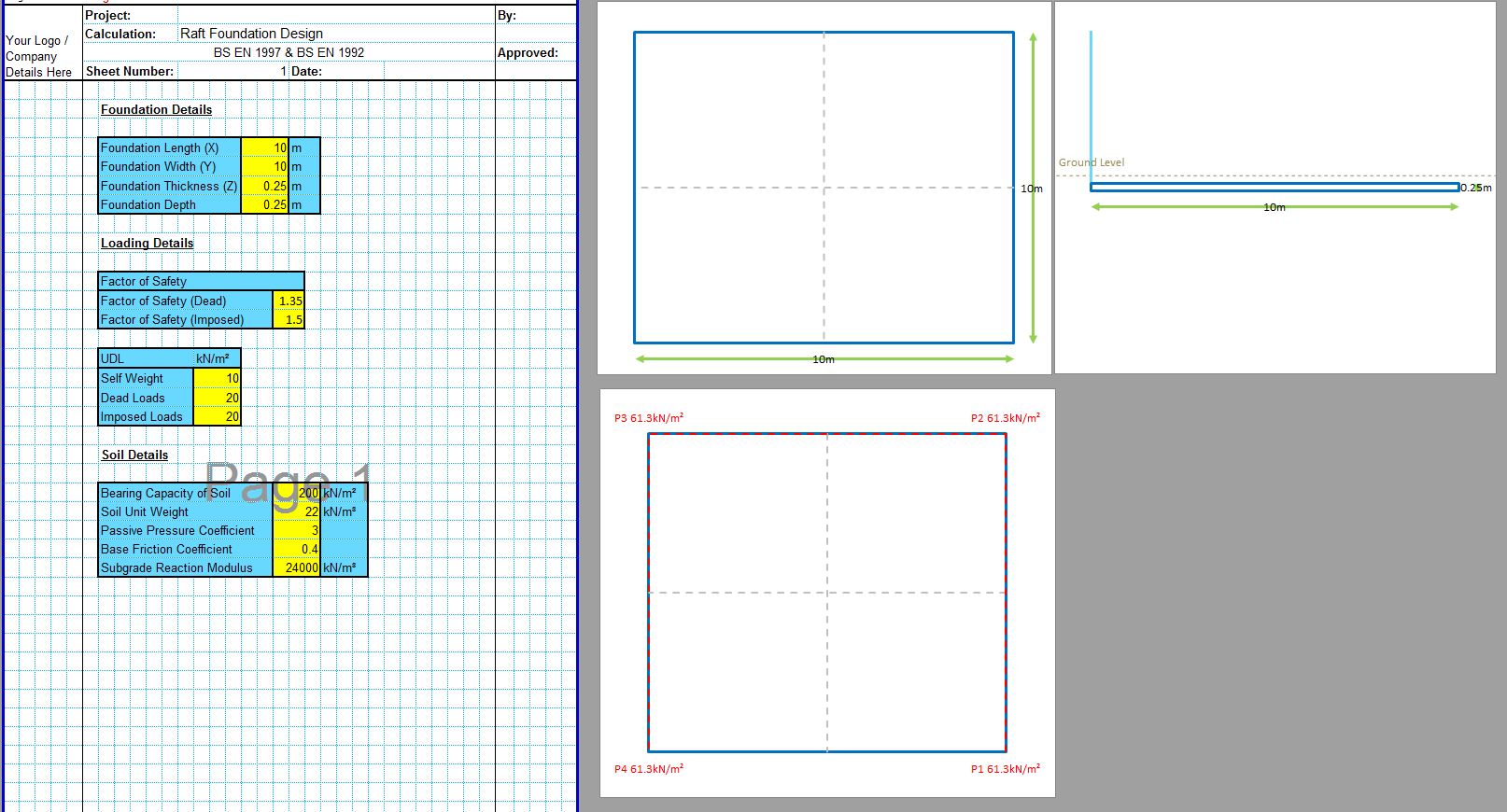
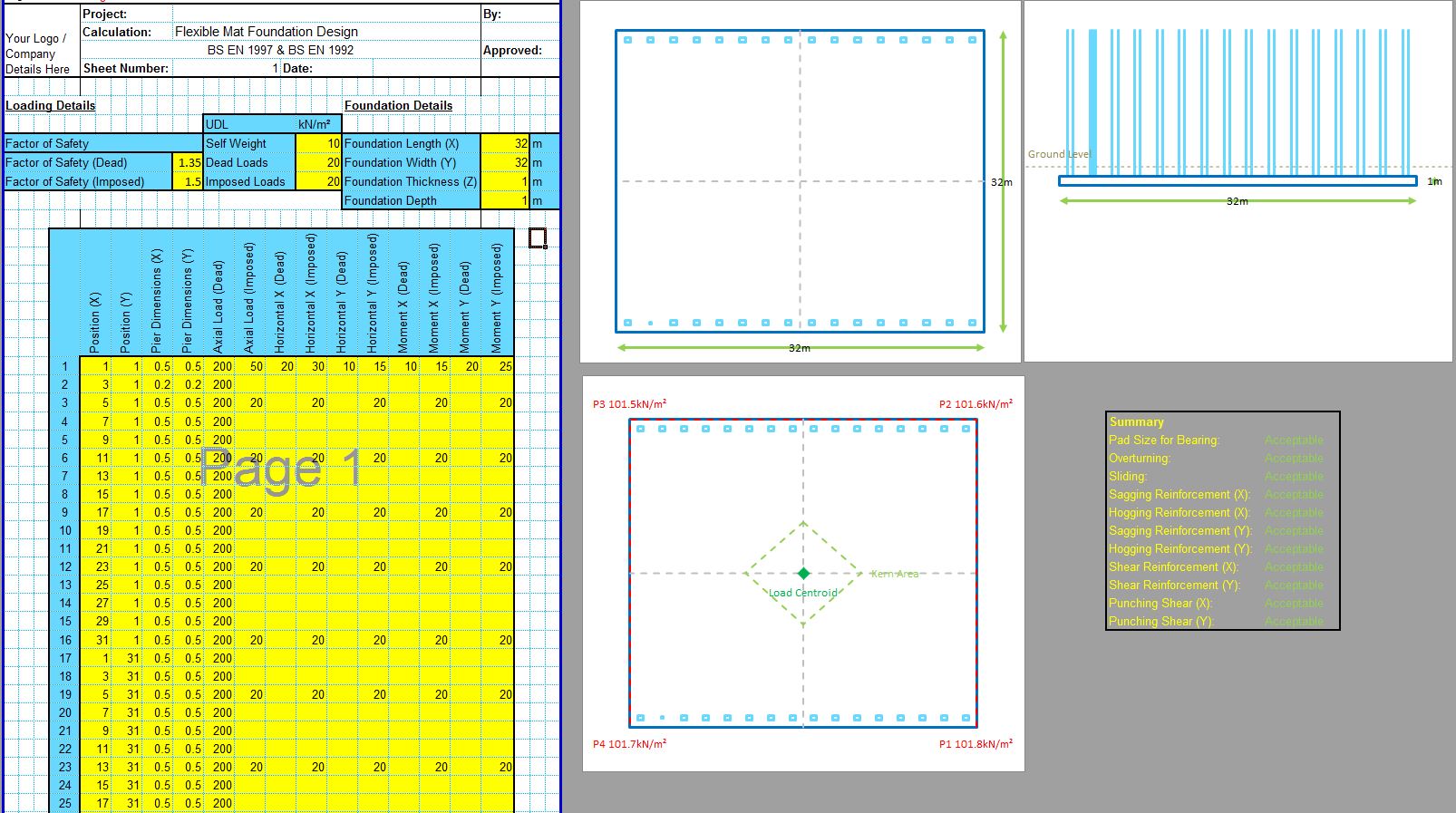
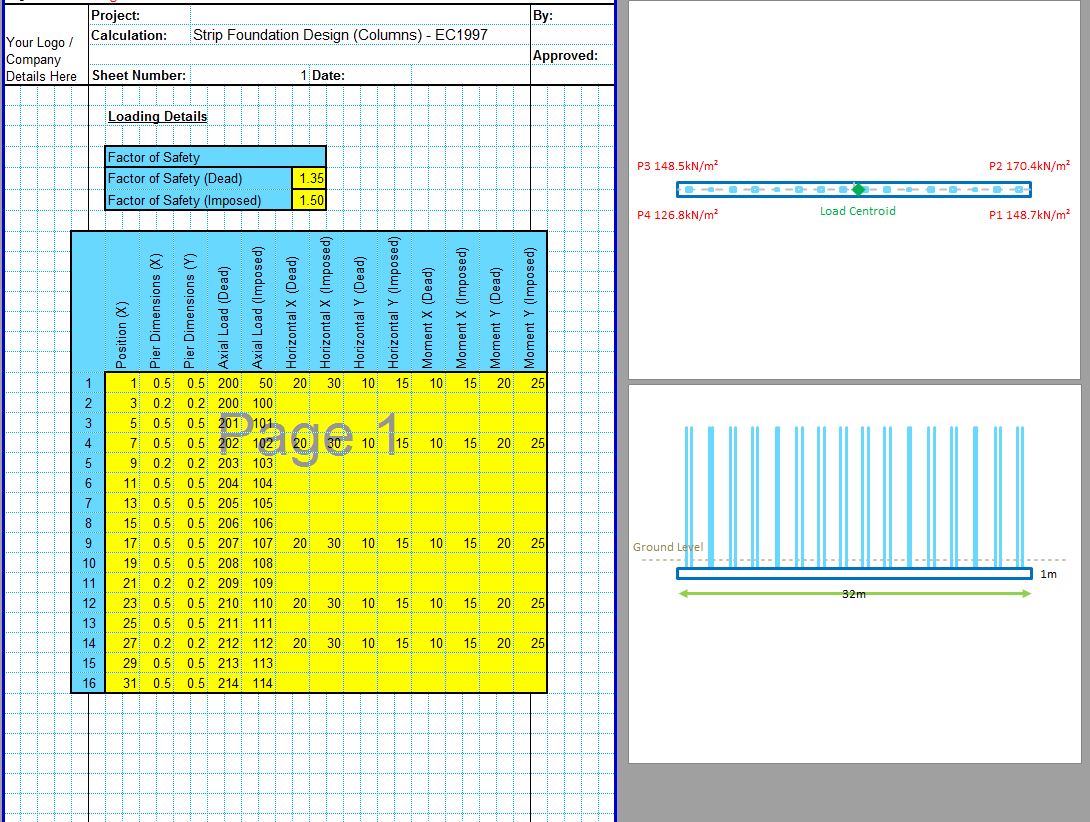
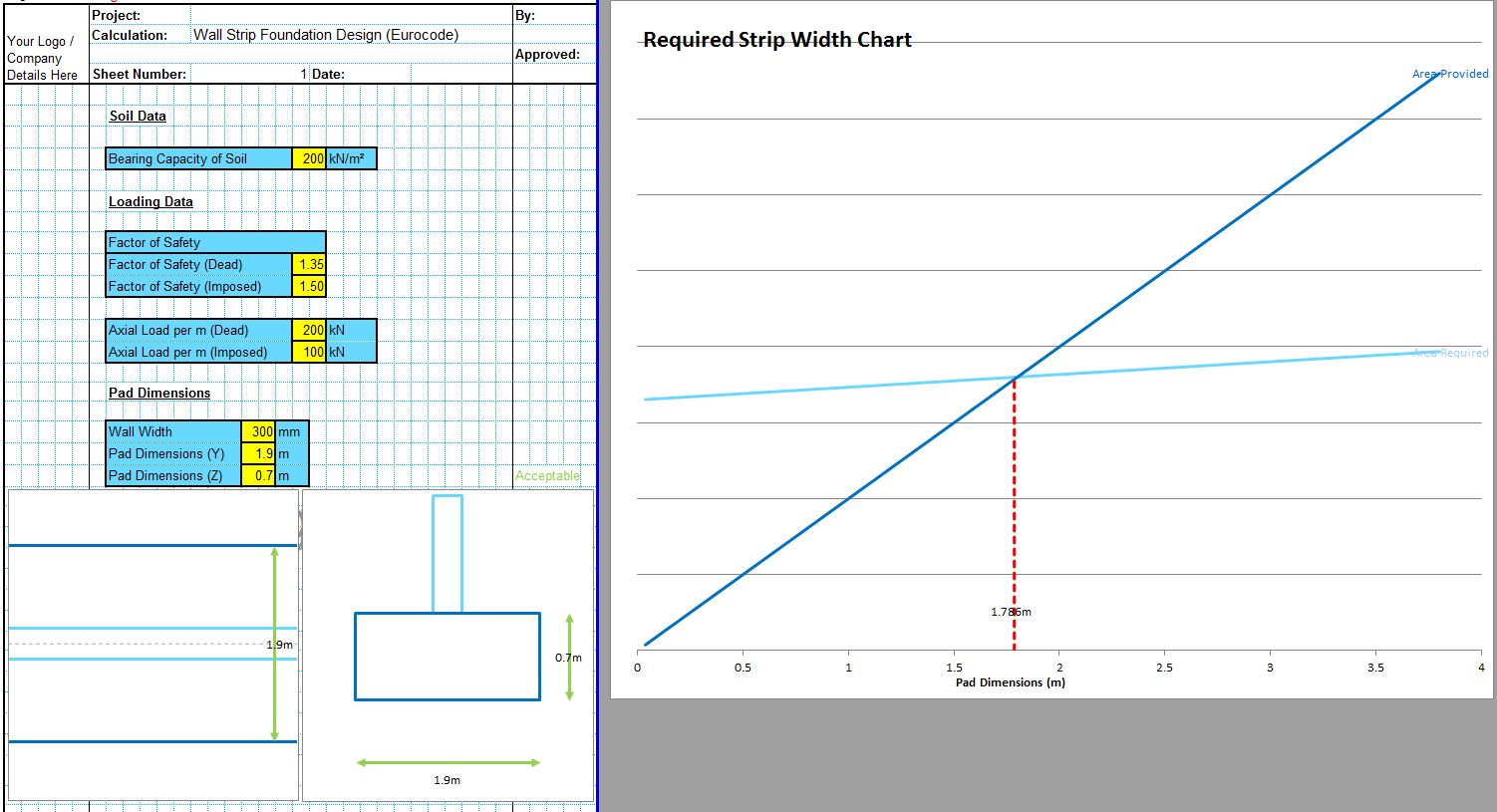
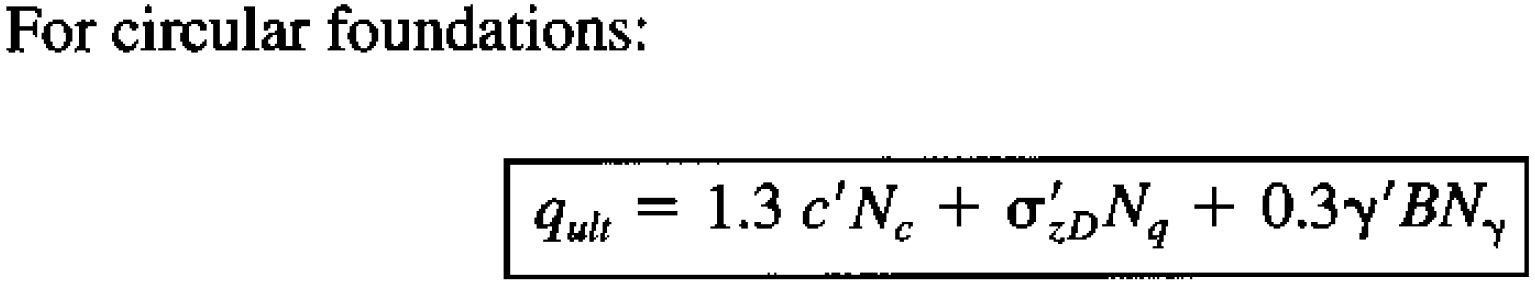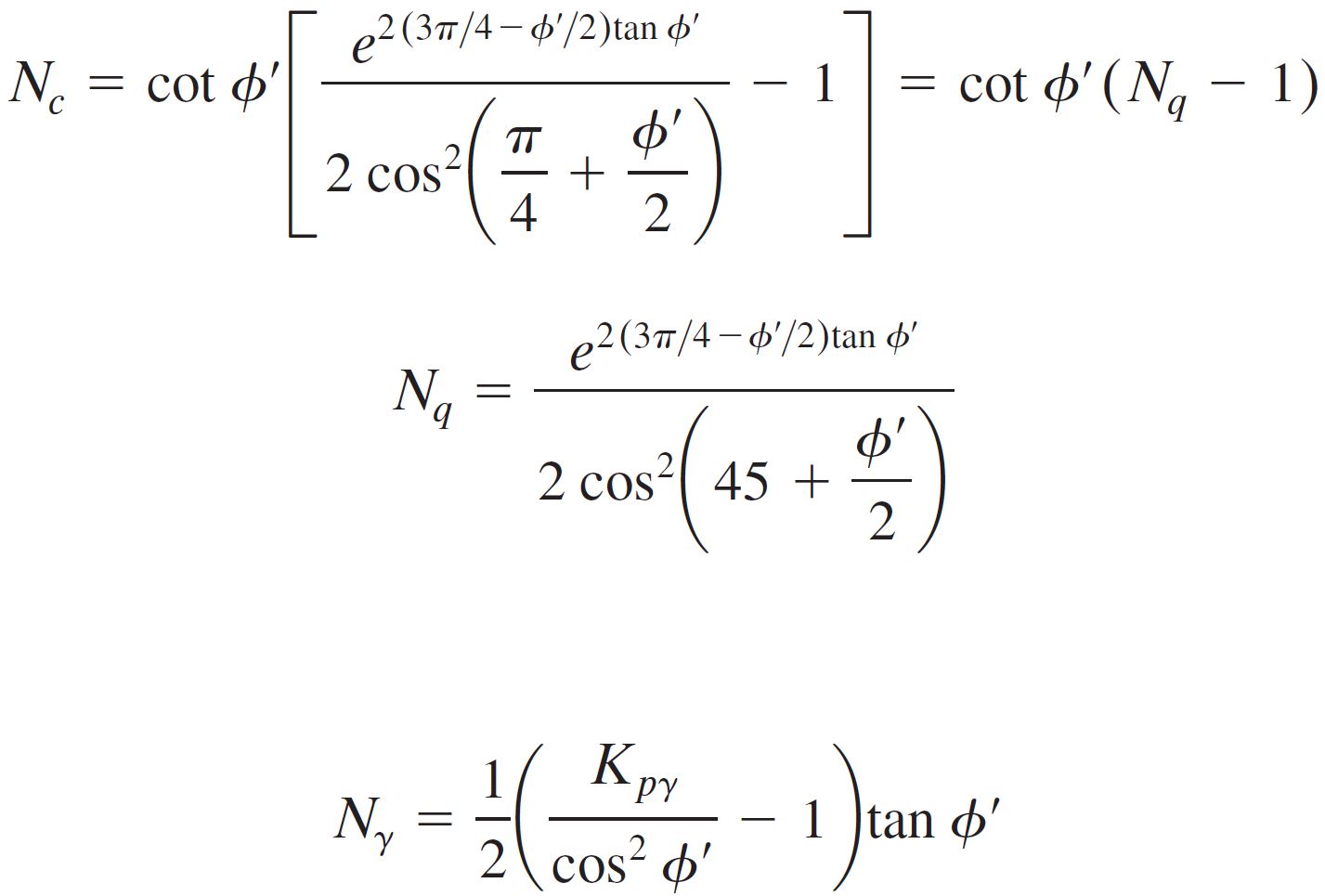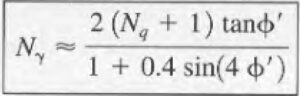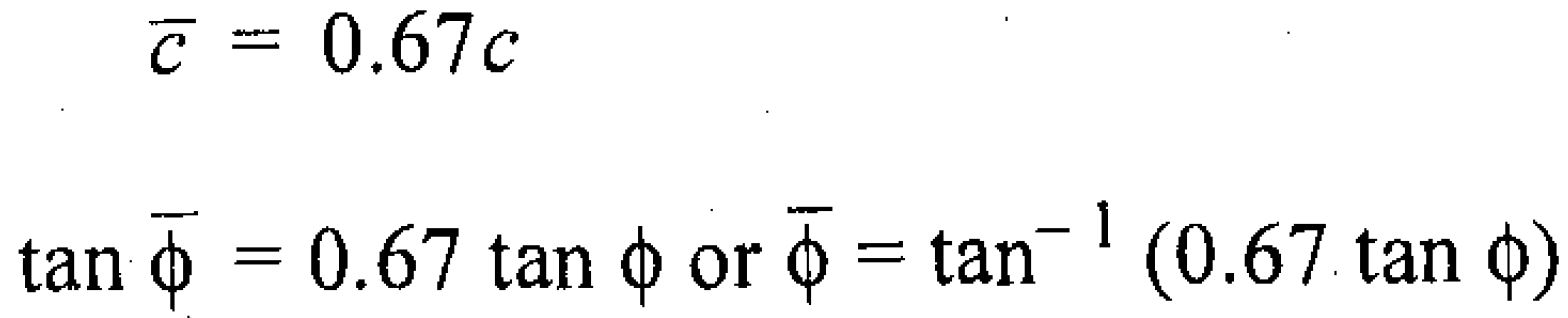The CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation Excel Suite includes the Terzaghi bearing capacity spreadsheet along with 5 other analytical methods and 3 methods based on site investigation information. The Terzaghi bearing capacity method was the first analytical method to be developed and while it has been extended many times, the Terzaghi method is still often used today. The CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation Excel Suite can be purchased at the bottom of this page for only £20.
Alternatively the Bearing Capacity Suite is also included in the full Foundation Design Suite which includes all 12 of our foundation design spreadsheets for only £50. This can also be purchased at the bottom of this page.
Terzaghi Bearing Capacity Theory
The earliest bearing capacity analysis method to be widely adopted was developed by Terzaghi. This is based on the work of Prandtl in the 1920s which was derived from the punching resistance of metals. Terzaghi adapted this work in the 1940s to apply the principles to the problem of shallow foundations bearing on soils.
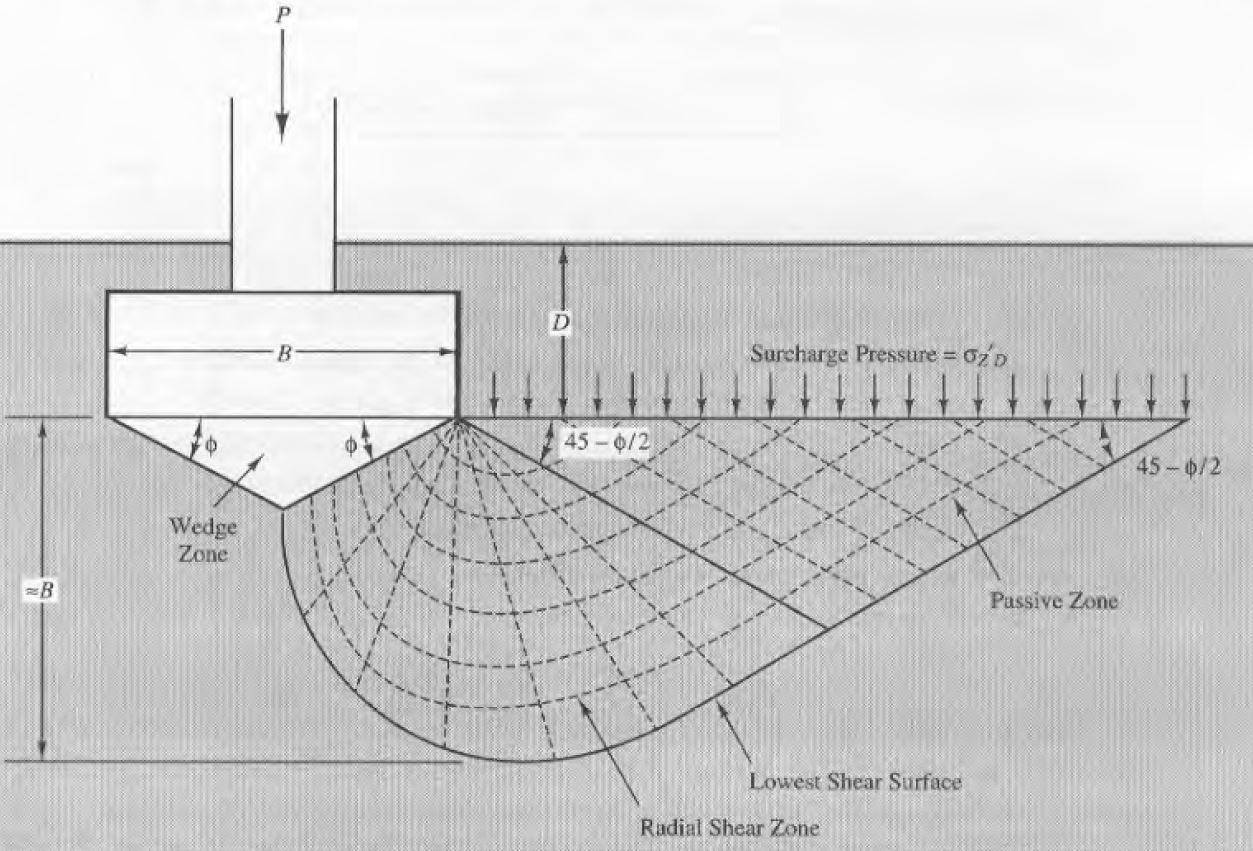
He used this plasticity theory and an assumed shear failure surface to calculate the required pressure to achieve shear failure in the soil. For his plastic analysis Terzaghi assumed that the failure surface of the soil would take the form shown in the below diagram.
Below the foundation a wedge of soil remains intact and is pushed downwards by the loads acting on the foundation. This wedge of moving soil creates a radial shear zone extending from each edge of the wedge. Terzaghi takes the shape of this radial shear zone as a series of logarithmic spirals. The third shear zone forms as a linear shear zone where the soils are able to shear along planar surfaces.
Terzaghi Bearing Capacity Equations
Terzaghi initial analysis of infinite strip foundations was later adapted to three equations which estimate the bearing capacity of the soil for square, circular or strip foundations. These equations take the common bearing capacity analysis form of three parts which consider the effects of soil cohesion, surcharge, and the weight of the soil.
The Terzaghi bearing capacity equations are shown below where the ultimate bearing capacity of the soil (qult) is dependant on the effective cohesion of the soil (c’), the effective friction angle of the soil, (Φ’), the vertical effective stress at depth D (σzD’), the effective unit weight of the soil (γ’), the depth of the foundation base (D) and the foundation width (B).
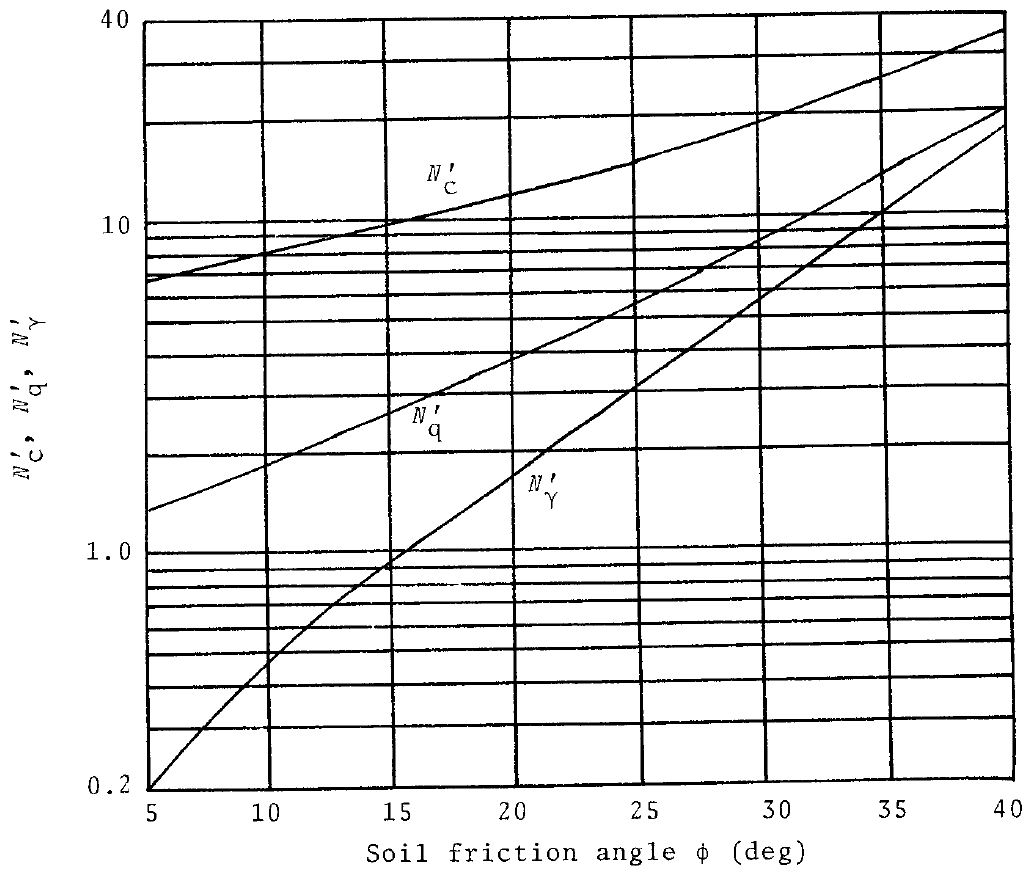
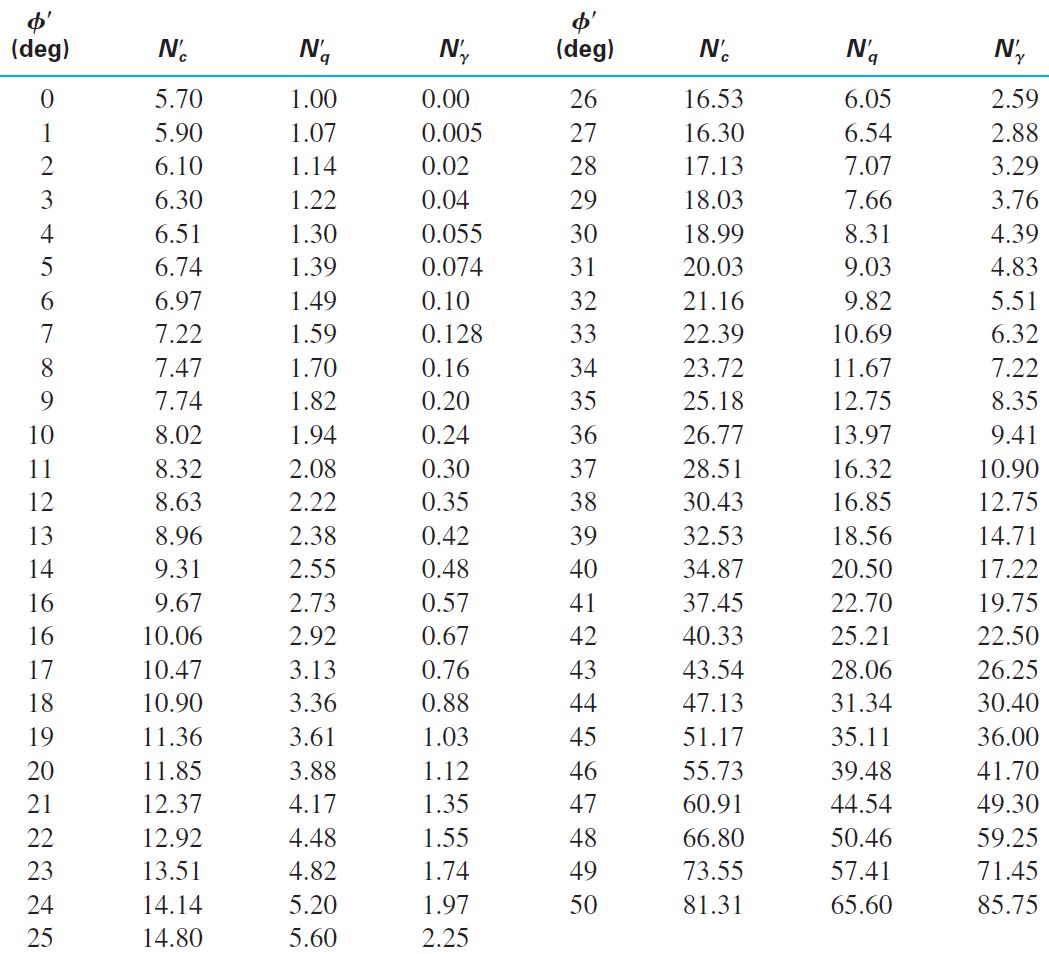
This includes the Terazghi bearing capacity factors Nc, Nq and Nγ. Terzaghi defined these bearing capacity factors using the below equations;
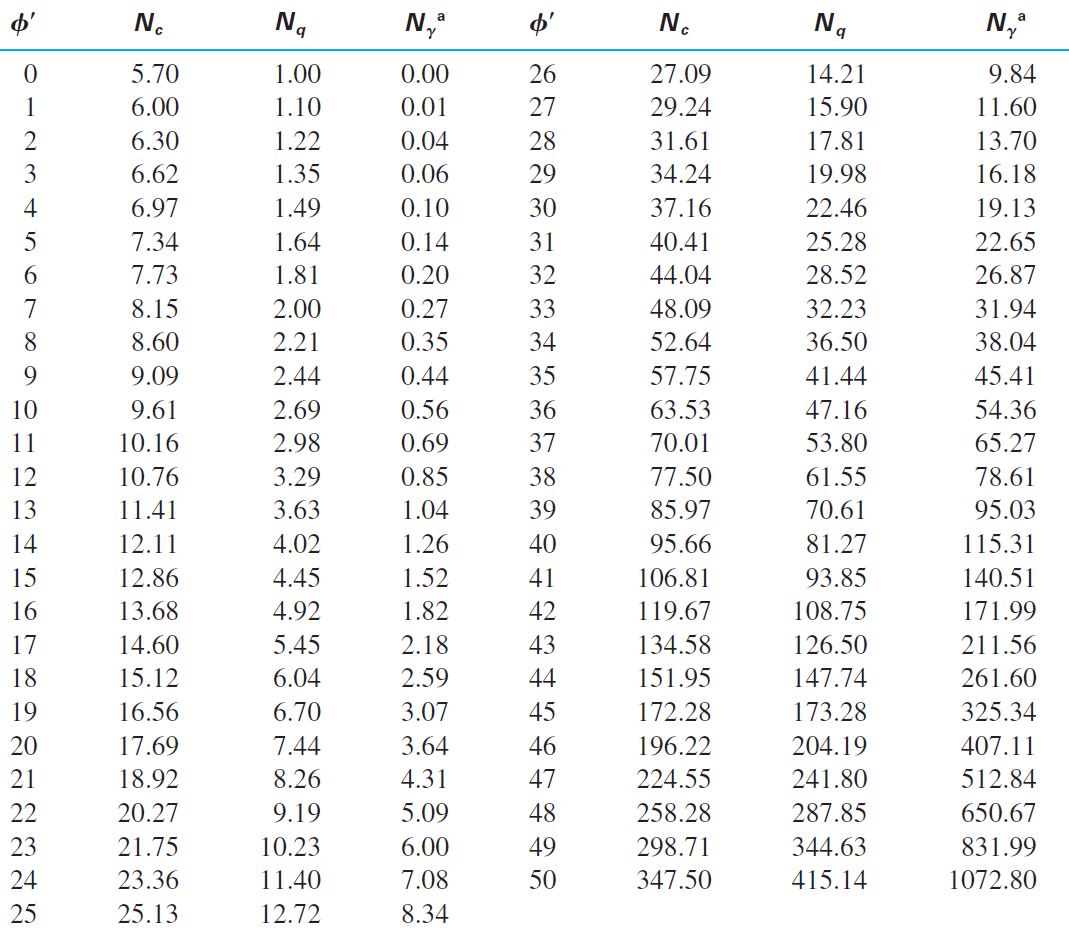
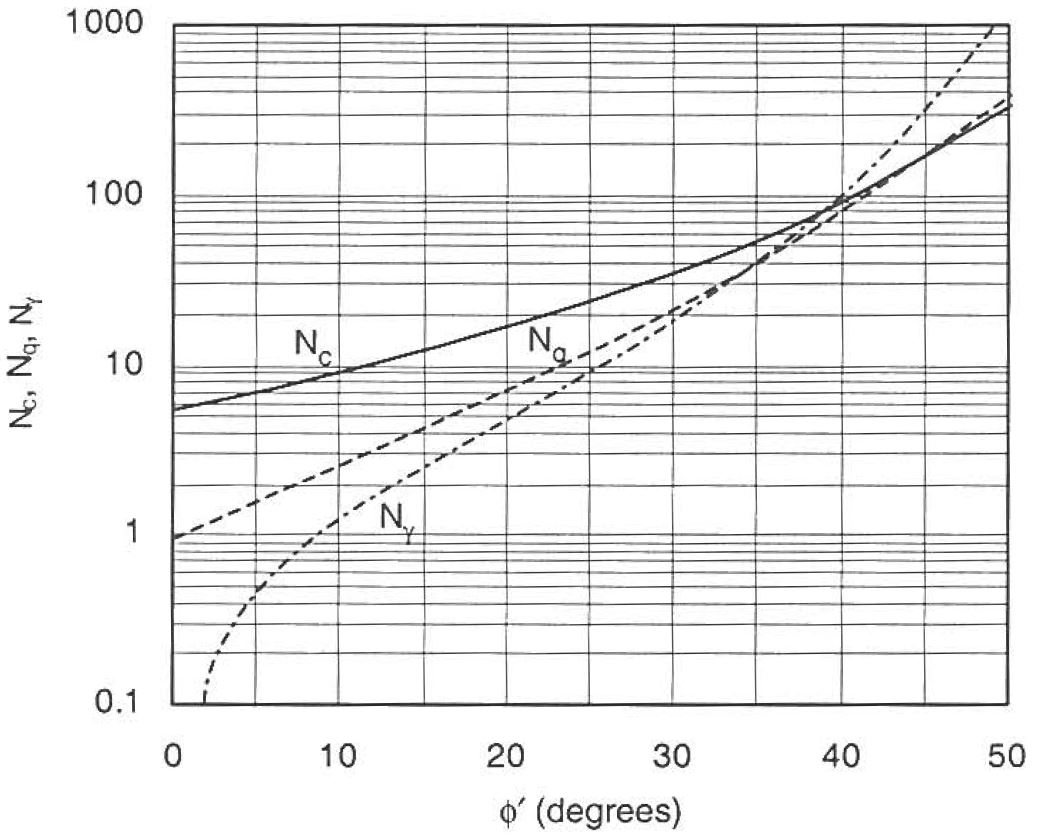
The Terzaghi bearing capacity factors have often been presented in tabular or graphical form in the past to simplify the calculations before computers. These tables and graphs are presented below.
Terzaghi calculated the value for Kpγ using graphical methods assuming that in practice his tabulated values for the Terzaghi bearing capacity factors would be used. The CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation Excel Suite uses a slightly simplified equation to calculate Nγ as shown below.
Terzaghi Bearing Capacity - Assumptions and Limitations
Terzaghi assumed the following parameters in order to model the shear failure of the soils beneath the foundation;
- The foundation is shallow, ie the depth is not greater than the width.
- The foundation is infinitely long. This allows Terzaghi to treat the foundation as a two dimensional problem which simplifies the analysis. Terzaghi later added shape coefficients to convert the results to suit finite square, circular or strip foundations.
- The base of the foundation is rough enough to prevent sliding between the foundation and the supporting soils. This is generally acceptable for most concrete foundations which are cast insitu.
- The supporting soils are modelled as a homogenous semi-infinite mass. This is of course often not appropriate, particularly not in soils with distinct layers. The shape of the failure surface means that only the soils between depth D and D + B need to be considered. The underlying soils are not considered and neither are the soils above the base of the foundation.
- The presence of any groundwater is assumed to be accounted for in the effective unit weight parameter.
- The shear strength of the soil is determined by the following equation;
- No consolidation of the soil occurs, settlement is only due to shearing and movement of the soil under the applied load.
- Terzaghi neglected to include the shear strength of the soils above the base of the foundation and treated them as simply an surcharge pressure from the soils self-weight. This assumption is conservative and causes the Terzaghi analysis method to break down for deep foundations. This also means that the strength or cohesion of these soils does not need to be considered in the analysis.
- The foundation is assumed to be much more rigid than the soil. Again this is often appropriate, particularly for isolated concrete pad foundations. Long strip foundations or large rafts can sometimes be modelled as flexible structures using the beam on an elastic foundation modeling methods.
- The applied loads are axial and act through the centroid of the foundations, and the ground is not sloping or close to any slopes. Again this is often appropriate though not always.
- Terzaghi modelled only the general shear failure mode, not local or punching shear failures. This is usually adequate as long as a suitable settlement analysis is also undertaken.
- The above equations are presented in terms of effective stresses. It is possible to convert this to a total stress analysis in cases where the soil conditions are saturated and undrained. This can be done by substituting the values for c’, Φ’ and σD’ for cT, ΦT and σD.
Local Shear Failure
Terzaghi also produced amended equations for calculating the bearing capacity of soils subject to local shear failure. This involves reducing the cohesion and the angle of internal friction using the following equations. These amended values are then used to calculate the Terzaghi bearing capacity factors in the same way as for the general shear failure conditions explained above.
Many graphs and tables have also been produced to illustrate the values for the bearing capacity factors for local failure in the same way as those for general shear failure. Examples of these tables and graphs are presented below.
Terzaghi Bearing Capacity - Conclusion
The Terzaghi bearing capacity analysis is still in use today, particularly for preliminary analysis. This is because the analysis is well known and relatively straightforward. It does not however take account of a number of common problems such as eccentric or inclined loading and has been improved several times over the following decades to increase the accuracy and increase the range of conditions which can be accommodated.
Generally the Terzaghi bearing capacity theory has been superseded by subsequent methods though the Terzaghi bearing capacity equation could still be used in simple cases where the design conditions are appropriate.
CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation Excel Suite
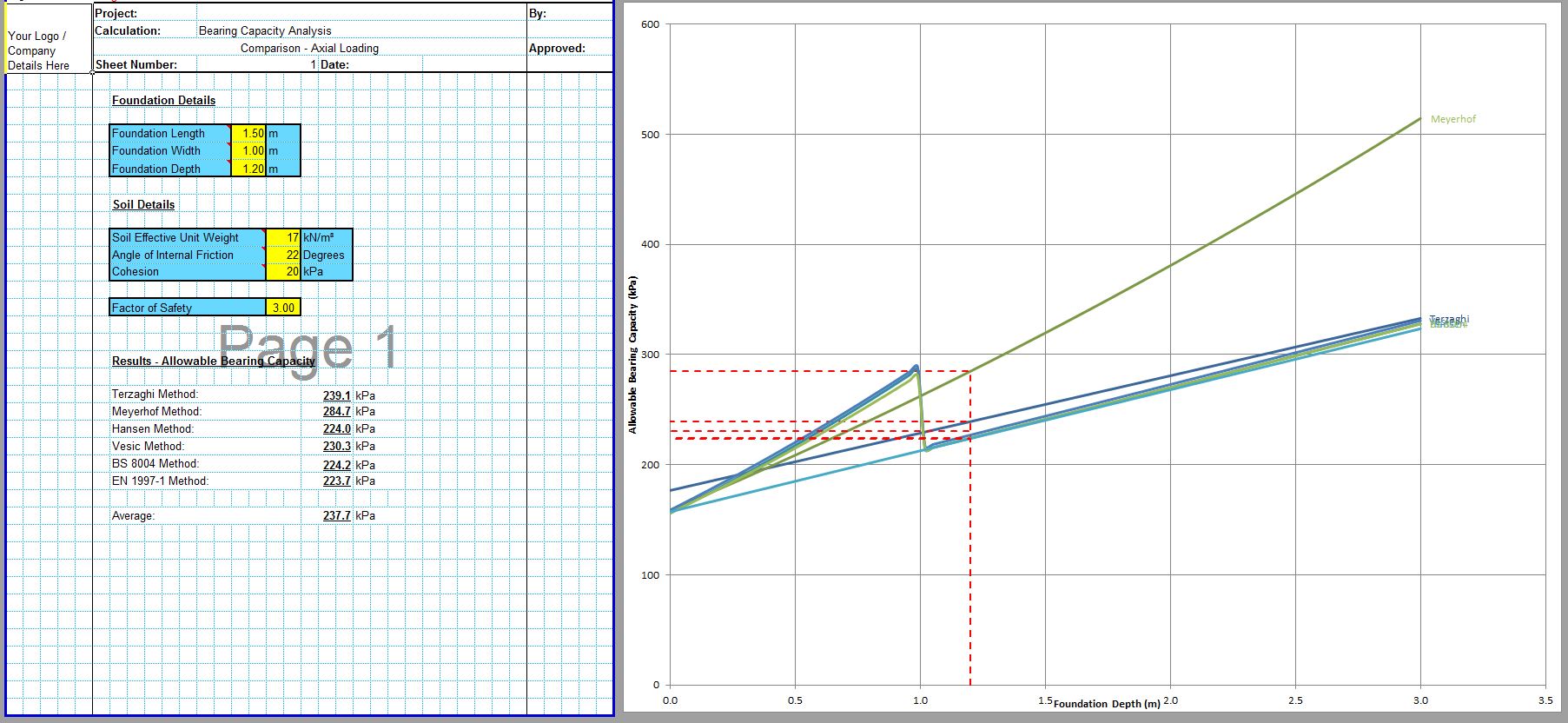
The CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation Excel Suite includes a Terzaghi bearing capacity spreadsheet. This spreadsheet suite includes 9 different methods of calculating the bearing capacity including both analytical methods and methods based on site investigation information. The spreadsheet suite also includes unique comparison tools which complete the bearing capacity calculations for all 6 analytical methods. This allows the designer to compare results and to choose the most appropriate bearing capacity value or even an average of all 6 methods.
Buy the CivilWeb Soil Bearing Capacity Calculation Excel Suite now for only £20.
Purchase the our Soil Bearing Capacity and Settlement Calculation Bundle for only £25.
Or buy our best value bundle, the full Foundation Design Suite including all 12 of our foundation design spreadsheets at a discount of 80%.
Download Free Trial Version
To try out a fully functional free trail version of this software, please enter your email address below to sign up to our newsletter.
Other Foundation Design Spreadsheets;
Foundation Design Spreadsheet Suite
Our full Foundation Design Suite includes all 12 of our foundation design spreadsheets for only £50 (80% discount).