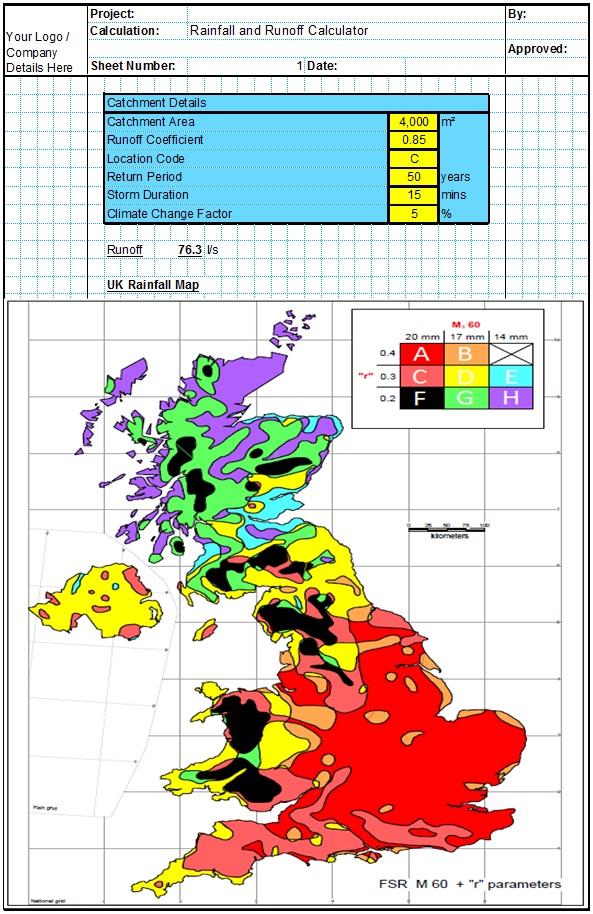
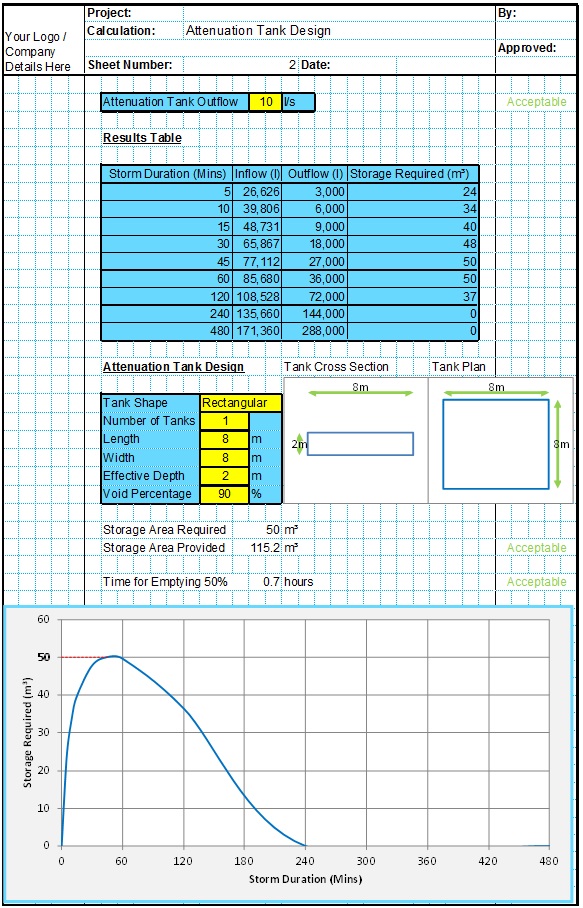
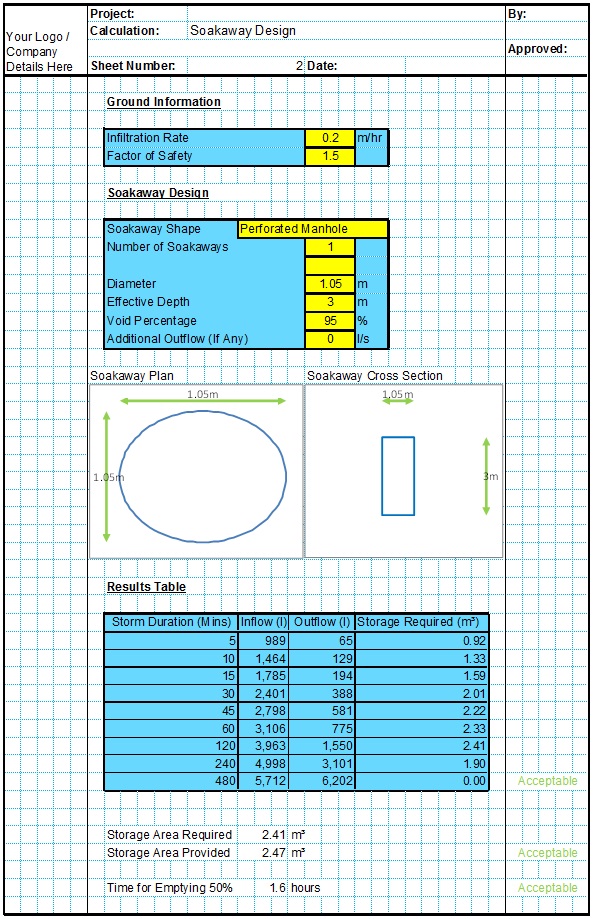
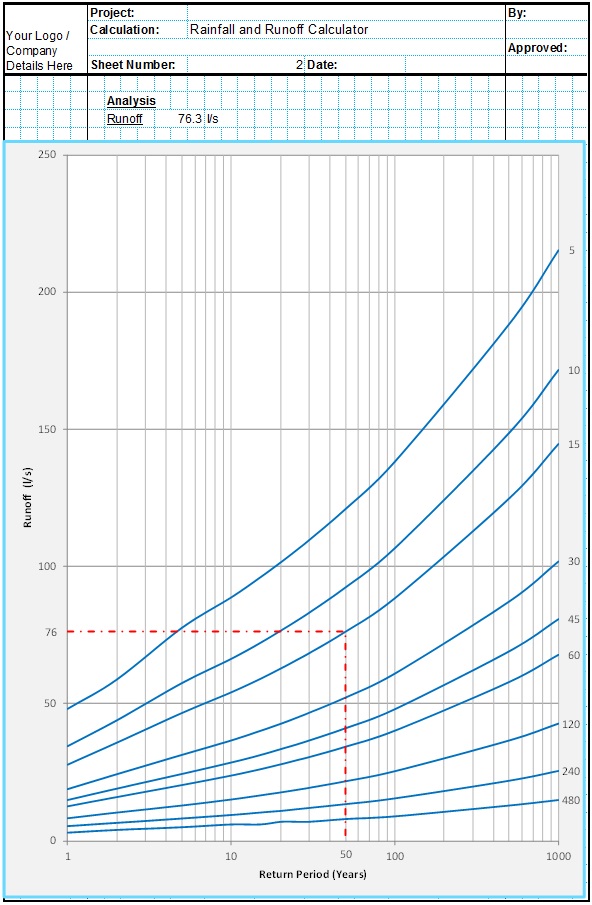
The Kerby equation is an empirical formula published in 1959 to estimate the time of concentration used in surface runoff design. The Kerby formula relates to overland flow for small catchments and shallow slopes.
Kerby Equation Calculations
Tc is the overland flow time of concentration (mins)
K is a units conversion coefficient, equal to 1.44 for SI units or 0.828 for US units
L is the overland flow length (m/or ft)
N is a dimensionless retardance coefficient
S is the dimensionless slope of the terrain conveying the overland flow.
Kerby Formula Applications
The Kerby formula is included in the CivilWeb Rainfall & Runoff Calculator package along with many other time of concentration formulas as it is still used in several design standards around the world, often in combination with a separate channel calculation such as Manning's Equation.
For larger catchments where the flow length exceeds 350m or well-defined channels are present, the Kerby equation should be supplemented with an estimation of the channel flow. For this reason in the US a combination of the Kerby formula and Kirpich equation is often used.
Related Spreadsheets from CivilWeb;
Runoff Calculator Spreadsheet
This spreadsheet calculates the design runoff flow for a site in accordance with the a number of different methods including the Wallingford Procedure.
Attenuation Design Spreadsheet
This spreadsheet calculates the requirements for a attenuation system and assists the user to design a suitable system.
Soakaway Design Spreadsheet
This spreadsheet calculates the requirements for a soakaway system and assists the user to design a suitable system.
Full Drainage Design Suite
Full drainage design suite (50% Discount) including 7 spreadsheets;
- Colebrook White Pipe Design
- Manning Pipe Design
- Manning Open Channel Design
- Linear Drainage Design
- Runoff Calculator
- Attenuation Design
- Soakaway Design