The CivilWeb Whitetopping Repair Design Spreadsheet is an advanced design spreadsheet which can be used to design whitetopping repairs for flexible pavements. The spreadsheet completes all the calculations required to assess the strength of the existing flexible pavement and the strength of the proposed whitetopping repair to determine the design life of the proposed pavement.
The spreadsheet can be used for conventional, thin or ultrathin whitetopping repairs. The spreadsheet includes unique analysis tools which display the expected performance of both the underlying asphalt pavement and the overlying whitetopping repair. This allows the designer to optimise the thickness of the whitetopping layer at a glance. This saves hours of work manually repeating the calculations for an iterative solution. The CivilWeb Whitetopping Repair Design spreadsheet can be purchased at the bottom of this page for only £10.
Alternatively, the Whitetopping Repair Design spreadsheet is also included in the CivilWeb Flexible Pavement Design suite which includes all 6 of our flexible road design spreadsheets. This can be purchased for only £20. Or our best value bundle is the full Pavement Design Excel Spreadsheets suite which also includes our Rigid Pavement Design suite for only £30.
What is Whitetopping?
Whitetopping is the common name for a new method of flexible road repair which involves installing a thin layer of concrete on top of the flexible road. This thin layer of concrete can be either bonded or unbonded to the underlying asphalt pavement. The thickness of the layer can vary from more than 200mm for unbonded whitetopping layers to 50mm or less for bonded whitetopping layers. Bonded whitetopping involves texturing the existing asphalt surface in order to promote a bond between the asphalt and the overlying concrete layer.
Whitetopping repair designs are sometimes divided into conventional, thin and ultrathin repairs. The CivilWeb Whitetopping Repair Design Spreadsheet can be used to design all three main types of whitetopping repairs.
Conventional whitetopping uses concrete thicknesses of around 150mm-200mm and is not bonded to the asphalt pavement below. This repair method essentially uses the underlying pavement as a stiff and stable base on which to install a new concrete road. These repairs are commonly undertaken when the underlying asphalt pavement has failed and whitetopping is seen as a cost effective method of replacement.
Thin whitetopping layers are typically around 100mm-150mm thick and are sometimes bonded to the underlying asphalt layers. Thin whitetopping repairs work together with the underlying pavement to create a composite pavement section. Thin whitetopping repairs are often undertaken to particularly heavily used sections of road such as intersections or junctions where rutting of the asphalt surface is an issue. The underlying pavement has not failed but is strengthened by the overlying concrete layer.
Ultrathin whitetopping repairs are typically between 50mm and 100mm thick though can be even thinner in some cases. Ultrathin whitetopping layers must be bonded to the underlying asphalt and act as a protective layer to the existing asphalt rather than a concrete slab supported by the underlying pavement. Ultrathin whitetopping repairs have only recently been used and are generally used as a low cost way to protecting low volume roads.
Whitetopping Repair Design
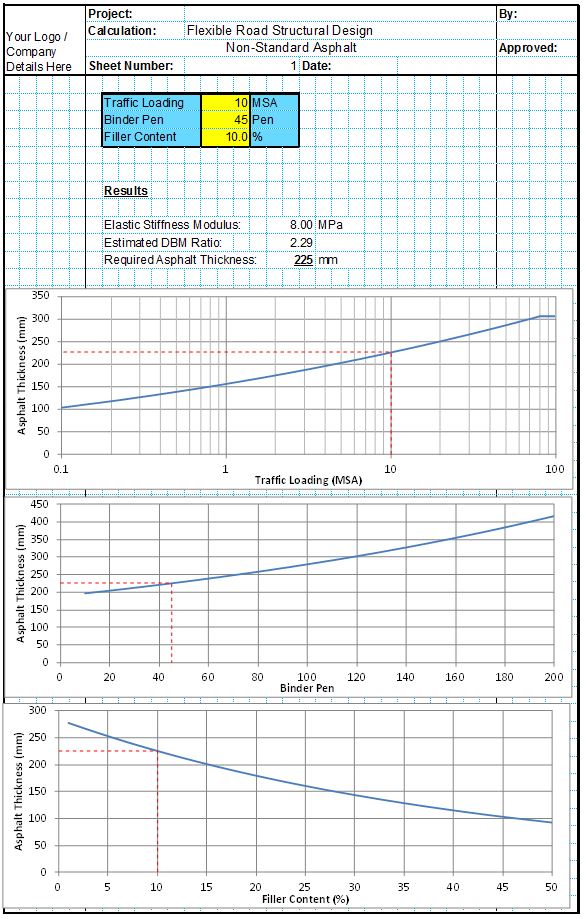
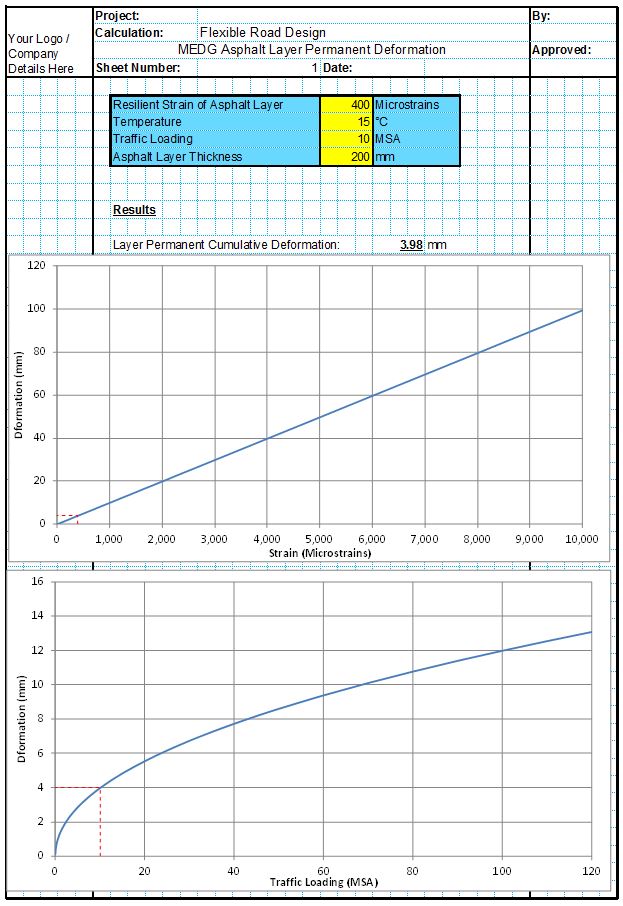
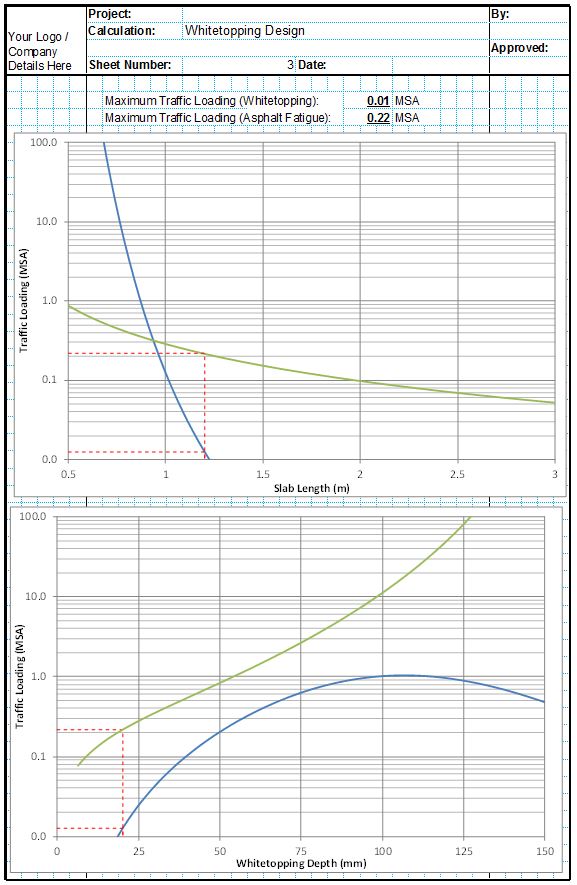
Whitetopping repair design can be a complex process. This is mainly due to the fact that the strength of the existing pavement and the thickness of the proposed whitetopping layer must be balanced in order to complete an optimised design. The thickness of whitetopping increases the expected design life of both the underlying asphalt and the concrete layers. However there is always a point at which adding further thickness to the whitetopping layer begins to lose effectiveness.
When completing the calculations by hand it can take many iterations to find the optimum whitetopping thickness which can take many hours of work. This thickness is also always different depending on the condition and thickness of the underlying asphalt layers. The CivilWeb Whitetopping Repair Design Spreadsheet allows the designer to see at a glance exactly what the optimum whitetopping thickness is.
Whitetopping Repair Design - Inputs
Firstly the designer must input the strength and condition of the existing asphalt pavement layers. The spreadsheet uses this to estimate the existing design life for the pavement. Next the designer must input a proposed whitetopping layer thickness, elasticity and strength. The spreadsheet uses this to determine the expected life for the whitetopping layer.
Next the designer must input some environmental inputs which the spreadsheet uses to calculate the environmental stresses which will be induced into the whitetopping layer. Finally the designer must specify the failure conditions and reliability of the required design. The spreadsheet uses these inputs to determine the expected design life of the composite pavement.
The spreadsheet then completes the calculations for the stresses which the whitetopping layer will need to accommodate and the expected design life for both the asphalt layer in fatigue and the whitetopping layer. The designer can then see at a glance exactly how thick the whitetopping layer needs to be to achieve the required design life.
CivilWeb Whitetopping Repair Design Spreadsheet
The CivilWeb Whitetopping Repair Design Spreadsheet completes the calculations required for a fully optimised whitetopping repair design. This saves the designer hours of hand calculations on every whitetopping repair design and allows a much more accurate design to be completed in minutes.
Buy the CivilWeb Whitetopping Repair Design Spreadsheet now for only £10
Or why not buy our full Flexible Pavement Design suite for only £20
Or buy our best value bundle, the full Pavement Design Suite including flexible and rigid pavement spreadsheets for only £30
Download Free Trial Version
To try out a fully functional free trail version of this software, please enter your email address below to sign up to our newsletter.